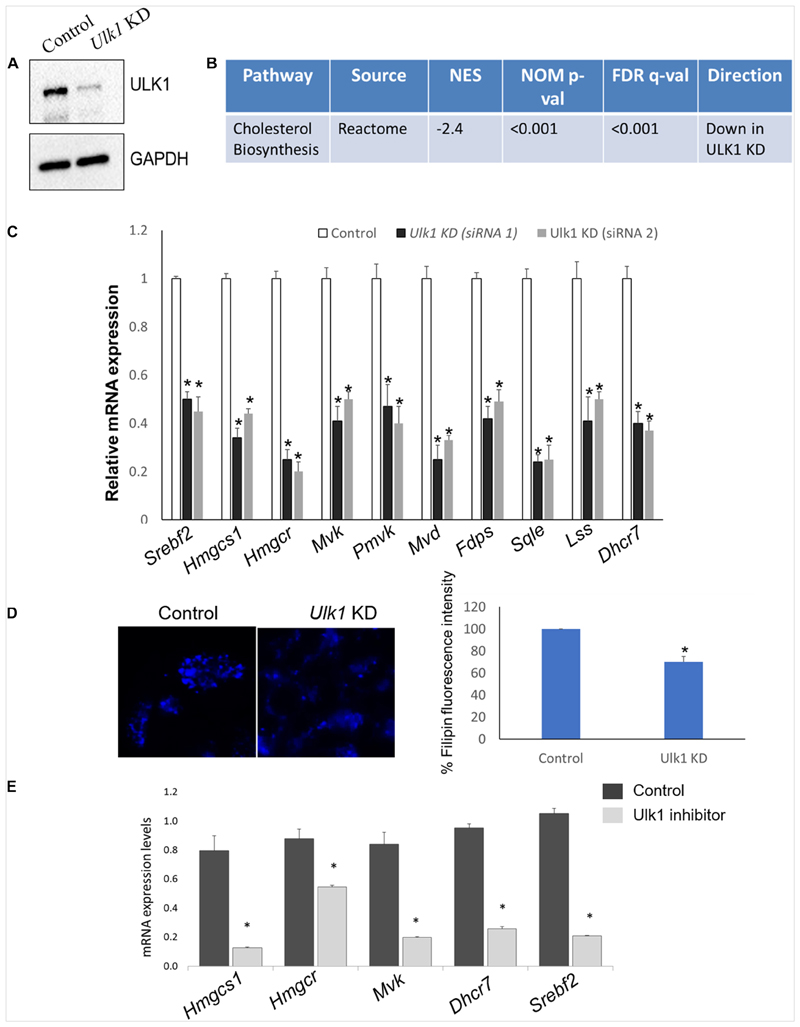
Figure 1. ULK1 regulates mevalonate/cholesterol biosynthesis pathway gene expression in mouse hepatocyte AML12 cells.
(A) Representative immunoblot showing knockdown (KD) efficiency of ULK1 in AML12 cells treated with ± Ulk1 siRNA (Thermo Fisher Scientific, s75753 siRNA #1; 10 nM/72 h) or a negative siRNA (denoted as Control). (B) Microarray derived transcriptomic pathway analysis in AML12 cells and mouse liver upon Ulk1 KD as described above. (C) qRT-PCR validation of mevalonate/cholesterol biosynthesis pathway genes ± Ulk1 siRNA’s 1 (Thermo Fisher Scientific s75753 siRNA #1) and 2 (Thermo Fisher Scientific s75751 siRNA #2) at 10 nM concentration for 72 h in AML12 cells. Values are means ± SD (n = 4) *p < 0.05. (D) Filipin staining and quantitation showing intracellular cholesterol levels in AML12 cells treated with ± Ulk1 siRNA (Thermo Fisher Scientific s75753 siRNA #1; 10 nM/72 h) or a negative siRNA (denoted as Control). AML12 cells upon Ulk1 KD (10 nM/72 h) were washed with PBS fixed and stained with filipin. All photographs were taken with the same exposure time and 20× magnification. (E) qRT-PCR validation of cholesterol biosynthesis genes enriched in the pathway analysis treated with SBI-0206965 (ULK1 inhibitor) at a dose of 10 uM for 48 h in AML12 cells. Values are means ± SD (n = 3,*p < 0.05).