Figure 2.
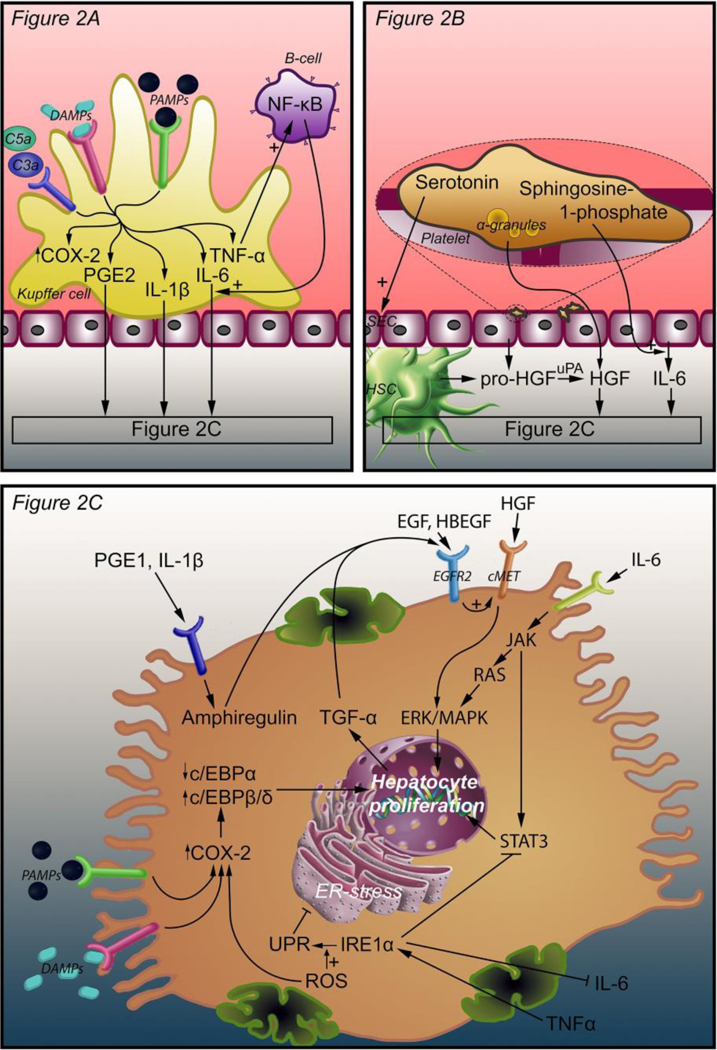
Intercellular and intracellular signals that initiate liver regeneration. Three mechanisms lead to hepatocyte proliferation. In response to complement factors C3a, C5a, PAMPs, and DAMPs, Kupffer cells release TNF-α, IL-6, PGE2, and IL-1β. TNF-α induces an autocrine loop through NF-κB production by B-cells. IL-6, PGE2, and IL-1β bind their cognate receptors on hepatocytes (A). Platelets accumulate in the space of Disse and release an armament of growth factors, including HGF, from their α-granules. Pro-HGF is released from SECs and HSCs and is converted to HGF by uPA, which is activated as a result of ECM damage after PHx. Platelets also release serotonin, which stimulates SECs, and sphringosine-1-phosphate to stimulate IL-6 release (B). PGE2 and IL-1β coming from Kupffer cells stimulate amphiregulin production in hepatocytes. HGF binds its receptor c-Met and activates hepatocyte proliferation through ERK-1/2 MAPK. IL-6 binds the IL-6 receptor and activates JAK, which induces hepatocyte proliferation through STAT3 and through the RAS-ERK-1/2 MAPK pathway. EGF, TGF-α, HBEGF, and amphiregulin enhance the effect of HGF through EGFR2. EGF is produced in the duodenum and reaches the liver through the portal circulation. TGF-α is produced by proliferating hepatocytes. HBEGF is released from monocytes and macrophages and converted to its active form by metalloproteinases. TNF-α (from Kupffer cells) and ROS enhance the UPR that is mediated by IRE1α. The UPR inhibits ER stress that in turn activates COX-2 expression. COX-2 is also stimulated by ROS, PAMPs, and DAMPs. Enhanced COX-2 expression increases C/EBPβ and C/EBPδ expression and decreases C/EBPα expression, thereby stimulating hepatocyte proliferation (C). Abbreviations: DAMPs, damage-associated molecular patterns; PAMPs, pathogen-associated molecular patterns; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B-cells; COX-2, cyclooxygenase 2; PGE2, prostaglandin E2; IL-1β, interleukin 1β; IL-6, interleukin 6; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor alpha; SEC, sinusoidal endothelial cell; HSC, hepatic stellate cell; HGF, hepatocyte growth factor; uPA, urokinase plasminogen activator; C/EBPα, β, and δ, CCAAT enhancer binding protein alpha, beta, and delta; TGF- α, tumor growth factor alpha; EGF, epidermal growth factor; EGFR2, epidermal growth factor receptor 2; JAK, Janus kinase; ERK, extracellular signal- regulated kinase; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; STAT3, signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; IRE1α, inositol-requiring enzyme-1α; UPR, unfolded protein response; ROS, reactive oxygen species.
