Figure 3. Two models for FhaB secretion: distal N-terminus versus hairpin.
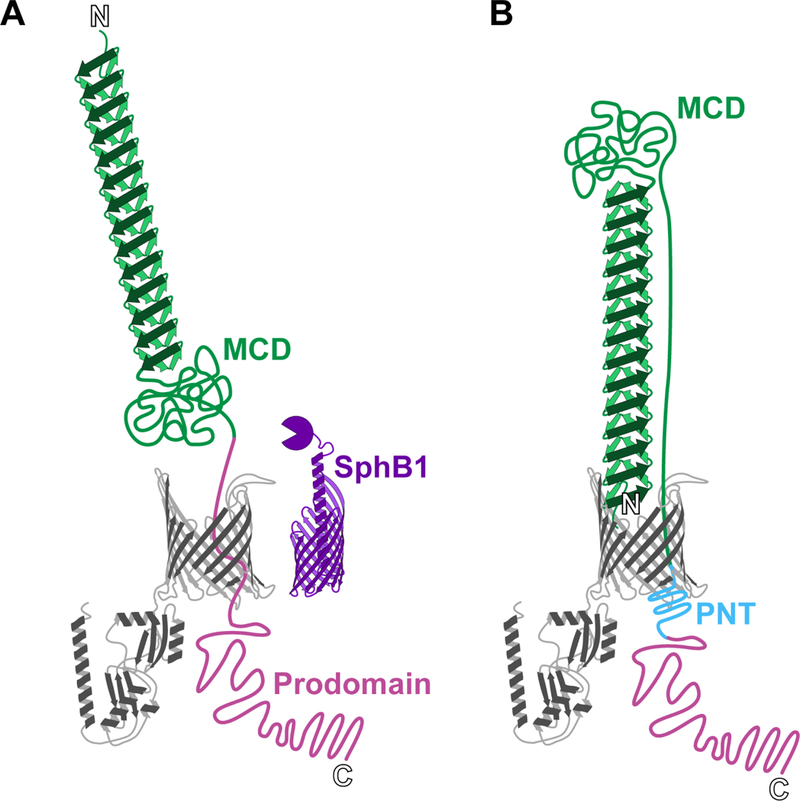
In the model proposed by Coutte et al. (A), the N-terminus of FhaB is pushed away from the membrane as more of the polypeptide translocates through FhaC. The protease SphB1 cleaves between the mature C-terminal domain (MCD) and the periplasmic prodomain, causing release of FHA. In the alternative “hairpin” model proposed by Mazar and Cotter (B), the N-terminus of FhaB remains bound to FhaC during secretion, and the MCD is located at the distal end of the β-helix. A portion of the MCD spans the helix length, as it is tethered to the periplasmic prodomain. The prodomain N-terminus (PNT) prevents translocation of the prodomain through FhaC.
