Figure 5.
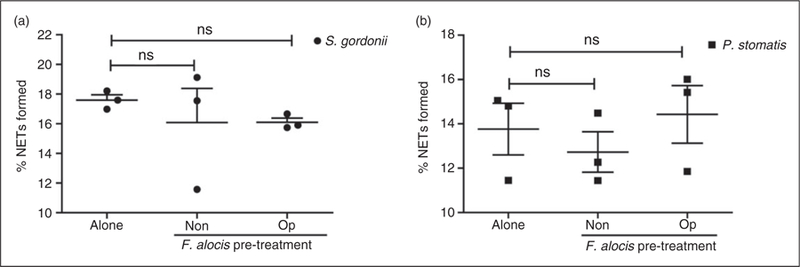
Pretreatment with F. alocis, in the presence or absence of serum, had no effect on either S. gordonii or P. stomatis-induced NETs. (a) Neutrophils were challenged with HI-labeled S. gordonii (MOI 100, Alone) for 180 min or pre-treated with non-opsonized (Non-op) or opsonized (Op) CFSE-labeled F. alocis for 60 min and then challenged with HI-labeled S. gordonii (MOI 100) for 180 min. (b) Neutrophils were challenged with HI-labeled P. stomatis (MOI 50, Alone) for 180 min or pre-treated with non-opsonized (Non-op) or opsonized (Op) CFSE-labeled F. alocis for 60 min and then challenged with HI-labeled P. stomatis (MOI 50) for 180 min. In both (a) and (b), following infection, cells were fixed, exposed to Abs directed against MPO (Red- AlexaFluor647), stained with DAPI, and then imaged for NET immunofluorescence by confocal microscopy. Quantification of percentage of NETs formed using ImageJ analysis. Data are expressed as means of % NETs ± SEM from three independent experiments. ns, non-significant.
