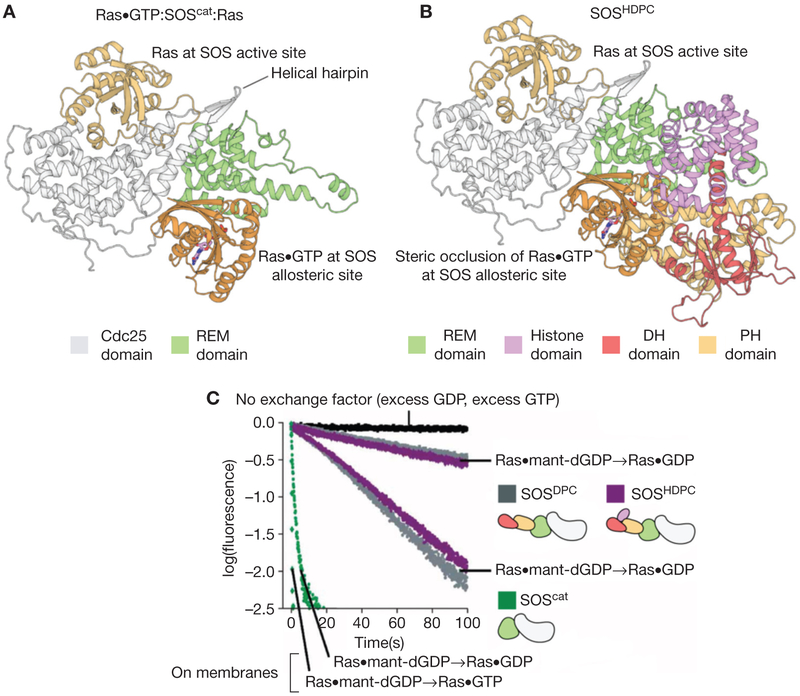
Figure 4.
The autoinhibition of Son-of-Sevenless (SOS) by regulatory domains. (A) The structure of the 2:1 Ras:SOScat complex, depicting Ras bound to the Cdc25 domain and Ras•GTP (guanosine triphosphate) bound to the allosteric site of SOS. (B) The structure of SOS containing the Dbl homology (DH)-Pleckstrin homology (PH) module and the catalytic module (SOSDPC) (Protein Data Bank [PDB] code: 3KSY) show that the DH-PH module sterically occludes the binding of Ras•GTP at the allosteric site. (C) Biochemical measurements show that SOSDPC has lower activity than SOScat. The fastest traces are for membrane-bound Ras (Gureasko et al. 2008). REM, Ras exchanger motif; GDP, guanosine diphosphate; dGDP, deoxyguanosine diphosphate.