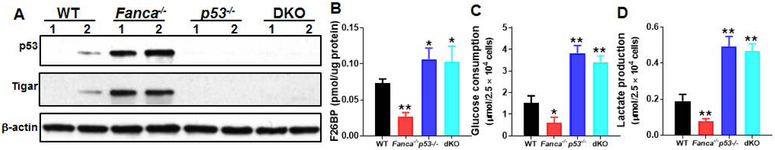
Fig 2. p53-dependent suppression of glycolysis in FA HSCs.
(A) Increased p53 and TIGAR proteins in FA HSPCs. Whole cell lysates (WCL) were extracted from 30,000 LSK isolated from WT, Fanca−/−, p53−/− or p53−/−Fanca−/− mice followed by immunoblotting using antibodies against p53, TIGAR, or β-actin. (B) Deletion of p53 increases F2,6BP level in Fanca−/− HSCs. SLAM cells isolated from WT, Fanca−/−, p53−/− or p53−/−Fanca−/− mice were subjected to MicroAssay for F26BP. (C, D) Deletion of p53 increases glucose consumption and lactate production in FA HSCs. SLAM cells isolated from WT, Fanca−/−, p53−/− or p53−/−Fanca−/− mice were subjected to glucose uptake (C) and lactate production analysis (D). Results depicted in B-D are means ± SD of three independent experiments. (n=6-9 per group). *, p<0.05; **, p<0.01.