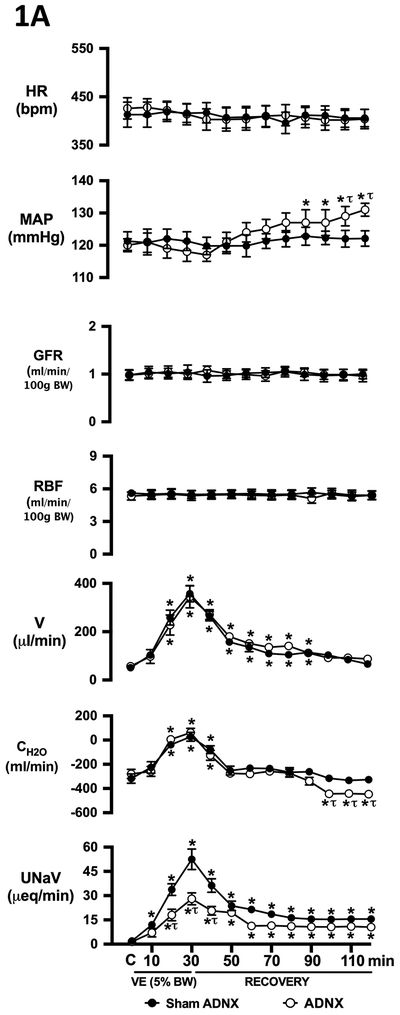
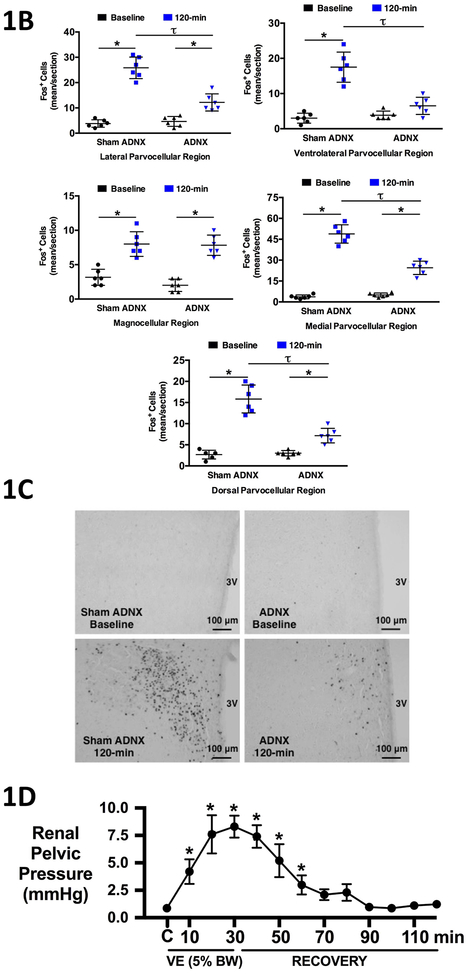
Figure 1. Effect of selective afferent renal nerve ablation on the cardiovascular, renal, and PVN neuronal responses to an acute volume expansion.
(A) Cardiovascular and renal responses to a 30-min 5% body weight isotonic saline volume expansion (VE) followed by a 90-min recovery period in conscious male Sprague Dawley (SD) rats 10 days after a selective afferent renal nerve ablation (ADNX) or sham ADNX procedure, (B) neuronal activation (c-fos-positive cell count) in the lateral parvocellular, ventrolateral parvocellular, magnocellular, medial parvocellular, and dorsal parvocellular regions of the paraventricular nucleus (PVN) of the hypothalamus following VE or a 2-h surgical recovery and control period (baseline group) in conscious male SD rats 10 days after a sham or ADNX procedure, (C) representative images from level 2 of the PVN and, (D) renal pelvic pressure [mmHg] in a separate group of anesthetized male Sprague Dawley rats during a control period (denoted C), a 30 minute 5% isotonic saline volume expansion (VE) period and a 90 minute recovery period. HR = heart rate (bpm), MAP = mean arterial pressure (mmHg), GFR = glomerular filtration rate (ml/min/100g body weight (BW)), RPF = renal plasma flow (ml/min/100g BW), V = urinary flow rate (μL/min), CH2O = free water clearance (ml/min), UNaV = urinary sodium excretion (μeq/min). N = 6/group. *p < 0.05 vs. group baseline value, denoted C; τp < 0.05 vs. respective sham ADNX value.