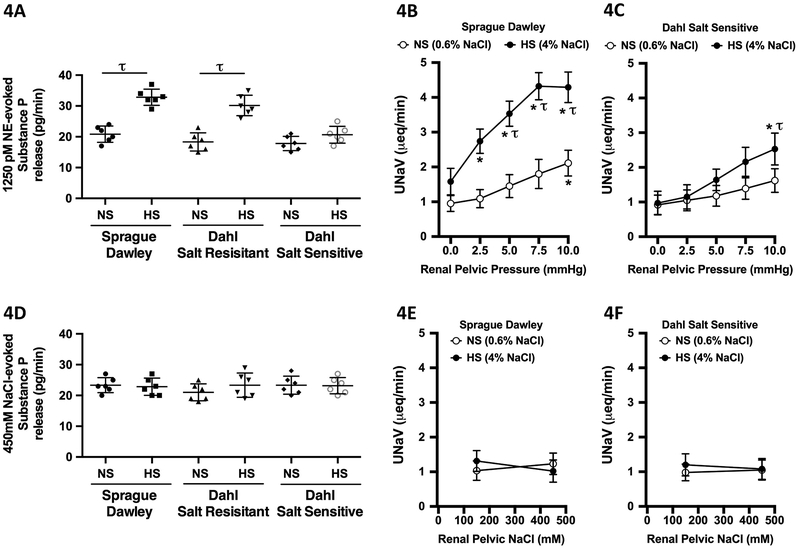
Figure 4. Effect of high salt intake on afferent renal nerve responsiveness.
(A) Ex-vivo renal pelvis substance P release (pg/min) in response to 1250 pM norepinephrine (NE) on day 21 of a normal salt (NS; 0.6% NaCl) or high salt (HS; 4% NaCl) diet in male Sprague Dawley (SD), Dahl Salt Resistant (DSR), and Dahl Salt Sensitive (DSS) rats and urinary sodium excretion (UNaV) in response to graded increases in renal pelvic pressure in male (B) SD and (C) DSS rats following a 21-day NS or HS diet, (D) ex-vivo renal pelvis substance P release in response to 450mM NaCl on day 21 of a NS or HS diet in male SD, DSR, and DSS rats and urinary sodium excretion in response to increased renal pelvic sodium concentration in male (E) SD and (F) DSS rats. N = 6/group. *p < 0.05 vs. group baseline UNaV with renal pelvic pressure at 0 mmHg, τp < 0.05 vs. respective NS group value.