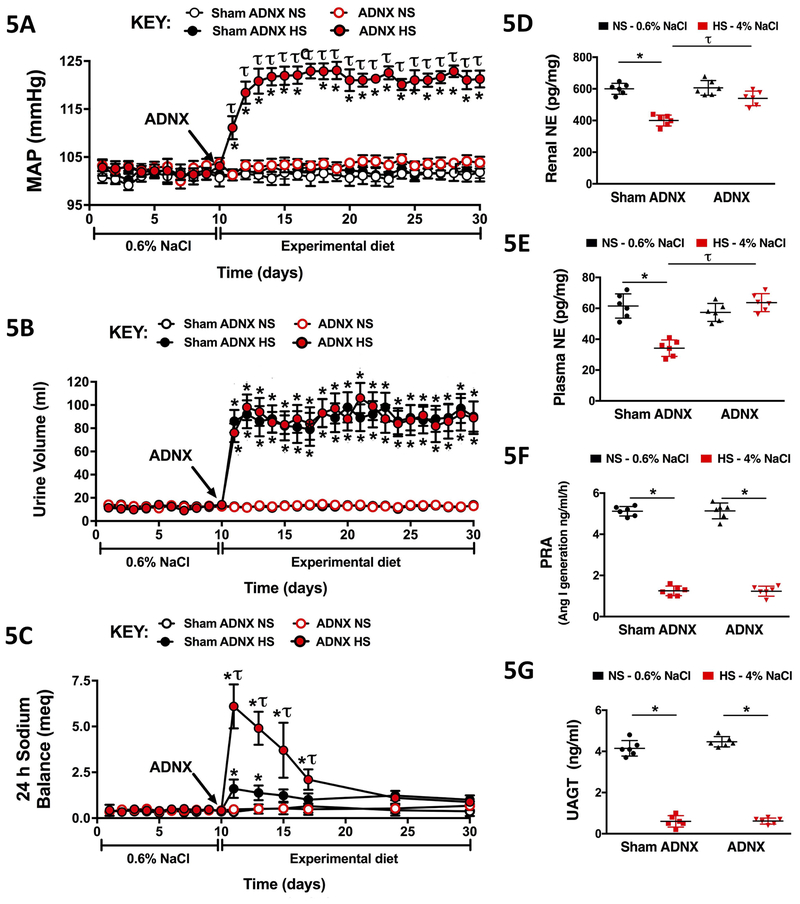
Figure 5. Effect of selective afferent renal nerve ablation on the cardiovascular, renal, and sympathetic responses to high salt intake in Sprague Dawley rats.
Daily (A) mean arterial pressure (MAP; mmHg), (B) 24-h urine volume (mL), and (C) 24-h sodium balance (meq) in male Sprague Dawley rats that underwent sham ADNX or ADNX immediately prior to a 21-day experimental normal salt (NS; 0.6% NaCl) or high salt (HS; 4% NaCl) diet and (D) renal norepinephrine (NE) content (pg/mg), (E) plasma NE concentration (nmol/L), (F) plasma renin activity (PRA; angiotensin I [ang I] generation, ng/ml/h) and (G) urinary angiotensinogen (UAGT; ng/ml) on day 21 of NS or HS intake. N = 6/group. *p < 0.05 vs. baseline (NS intake); τp < 0.05 vs. respective sham ADNX group.