Figure 4. Comparison of the fT3SS from B. burgdorferi and the vT3SS from Salmonella.
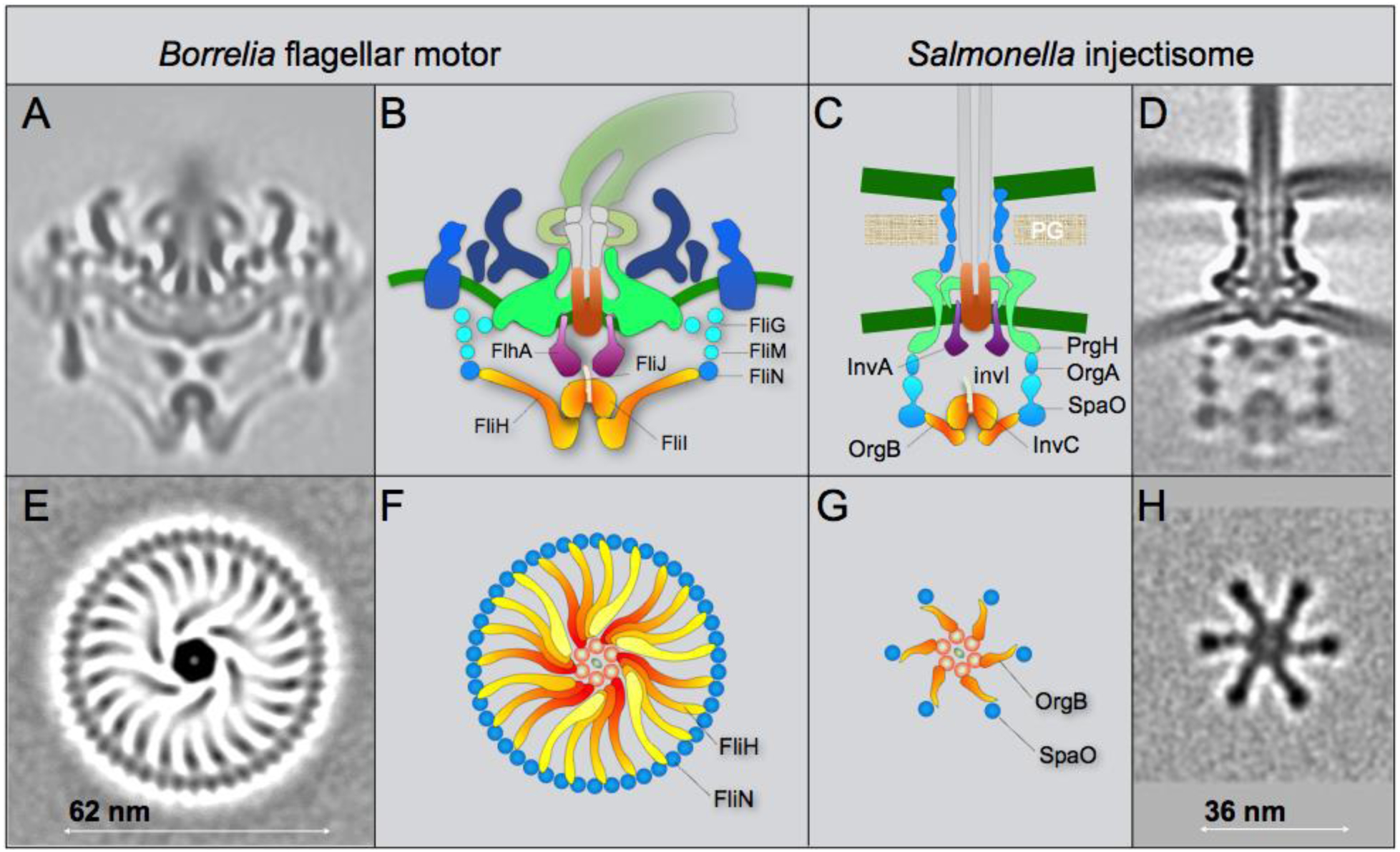
(A) A central section from the B. burgdorferi motor. (B) The fT3SS in the spirochete motor includes the ATPase complex (orange) and the export apparatus (purple) underneath the MS-ring. (C, D) The vT3SS from Salmonella injectisome is modeled in a similar color scheme. The difference between the two T3SSs is striking in a comparison of the cross-sections of their ATPase complexes. Note that the C-ring from the B. burgdorferi motor is a continuous ring with ~46 copies of FliN tetramer. There are 23 visible FliH spokes (E, F). There are six pods in Salmonella injectisome. Only six spokes of the FliH homolog OrgB connect the ATPase complex to the SpaO molecules that compose the pod of the injectisome. Adapted from prior publication (Qin et al., 2018), with permission.
