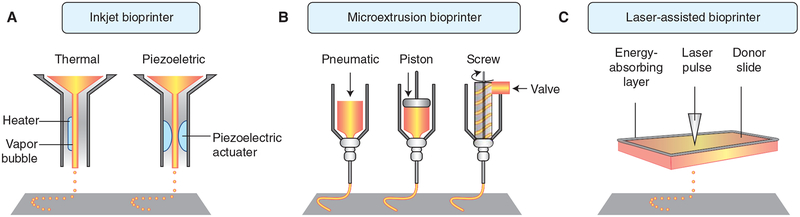
Figure 2.
Components of inkjet, microextrusion, and laser-assisted bioprinters. (A) Thermal inkjet printers electrically heat the printhead to produce air-pressure pulses that force droplets from the nozzle, whereas acoustic printers use pulses formed by piezoelectric or ultrasound pressure. (B) Microextrusion printers use pneumatic or mechanical (piston or screw) dispensing systems to extrude continuous beads of material and/or cells. (C) Laser-assisted printers use lasers focused on an absorbing substrate to generate pressures that propel cell-containing materials onto a collector substrate. (From Murphy and Atala 2014; adapted, with permission, from Nature Publishing Group © 2014.)