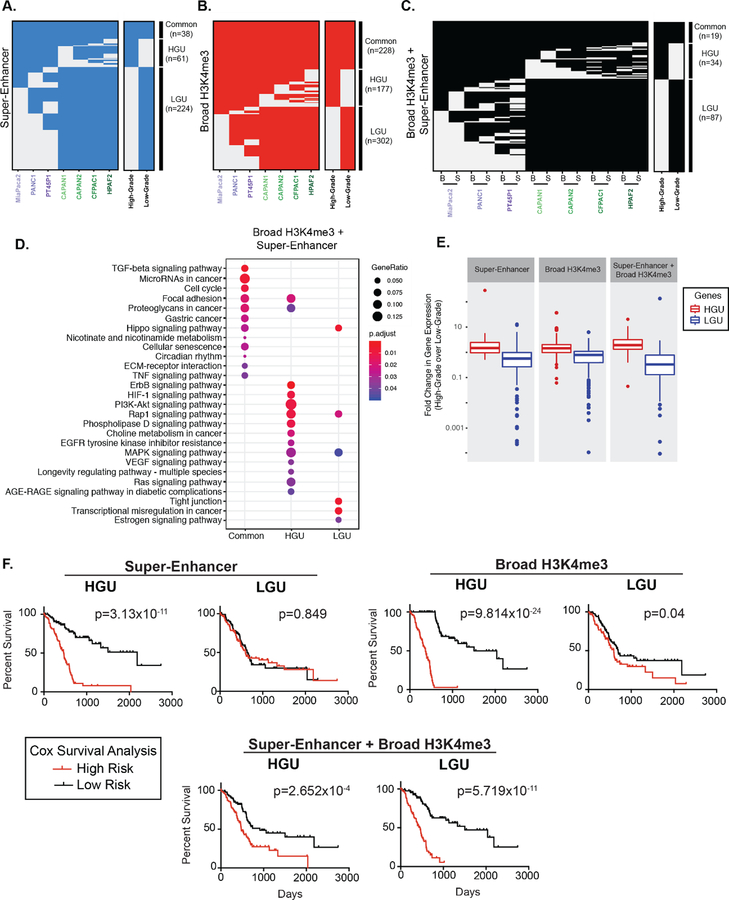
Figure 2.
Broad domains mark distinctive pathways and are predictive of poorer PDAC patient survival. (A) Clustering of genomic regions encompassing super-enhancers across seven human PDAC cell lines to define common, High- and Low-Grade unique super-enhancers. (B) A similar analysis was performed on broad H3K4me3 domains to define common, High- and Low-Grade unique (HGU and LGU, respectively) broad H3K4me3 domains. (C) A similar analysis was performed to look at overlapping domains, where ‘B’ represents Broad H3K4me3 domains and ‘S’ represents super-enhancers. (D) Gene Ontology pathway enrichment profiles of genes marked by both domains that are common, HGU or LGU domains. (E) Comparison of expression levels of genes marked by the indicated domains in High-Grade and Low-Grade PDAC cells. Data is derived from mean normalized expression counts of genes. (F) Kaplan-Meier survival analysis of high- and low-risk groups (red and black, respectively) for genes marked High-Grade unique (HGU) and Low-Grade unique (LGU) domains for the indicated domain type.