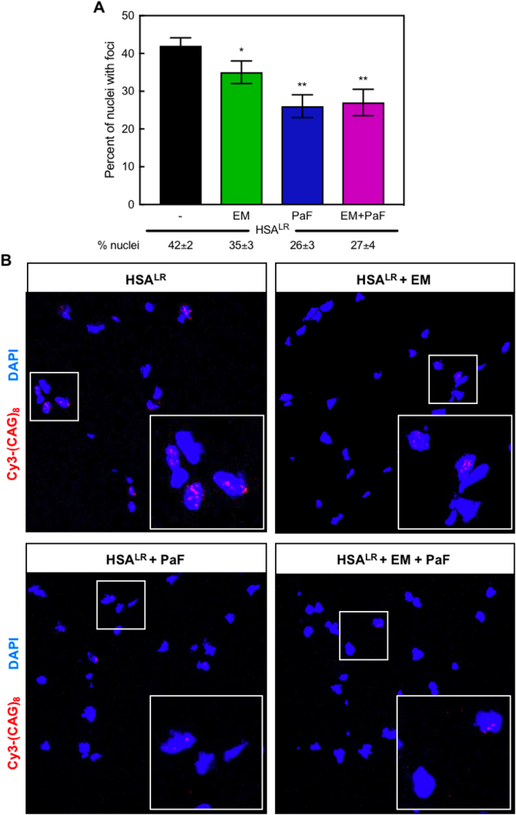
Figure 7. Combination treatment reduces ribonuclear foci-positive nuclei in the HSALR DM1 mouse model.
(A) Quantification of the percent of nuclei with ribonuclear foci in quadriceps muscle of HSALR mice determined via in situ hybridization of CUG-repeat RNA. A reduction in the percent of nuclei with ribonuclear foci was observed with treatments of 600 mg kg−1 erythromycin (EM, green) or 10 mg kg−1 pafuramidine (PaF, blue) or a combination of both (EM+PaF, magenta) per oral administration daily for 14 days. Mean percent of nuclei with ribonuclear foci ± standard deviation values are displayed below each graph. (B) Fluorescent in situ hybridization microscopy in quadriceps muscle of untreated (HSALR), erythromycin (EM), pafuramidine (PaF) and combination-treated (HSALR + EM + PaF) HSALR mice against CUG RNA using a Cy3-(CAG)8 probe (red). DAPI shown in blue. Larger box inset in lower righthand corner is magnification of smaller boxed region to clearly show foci.