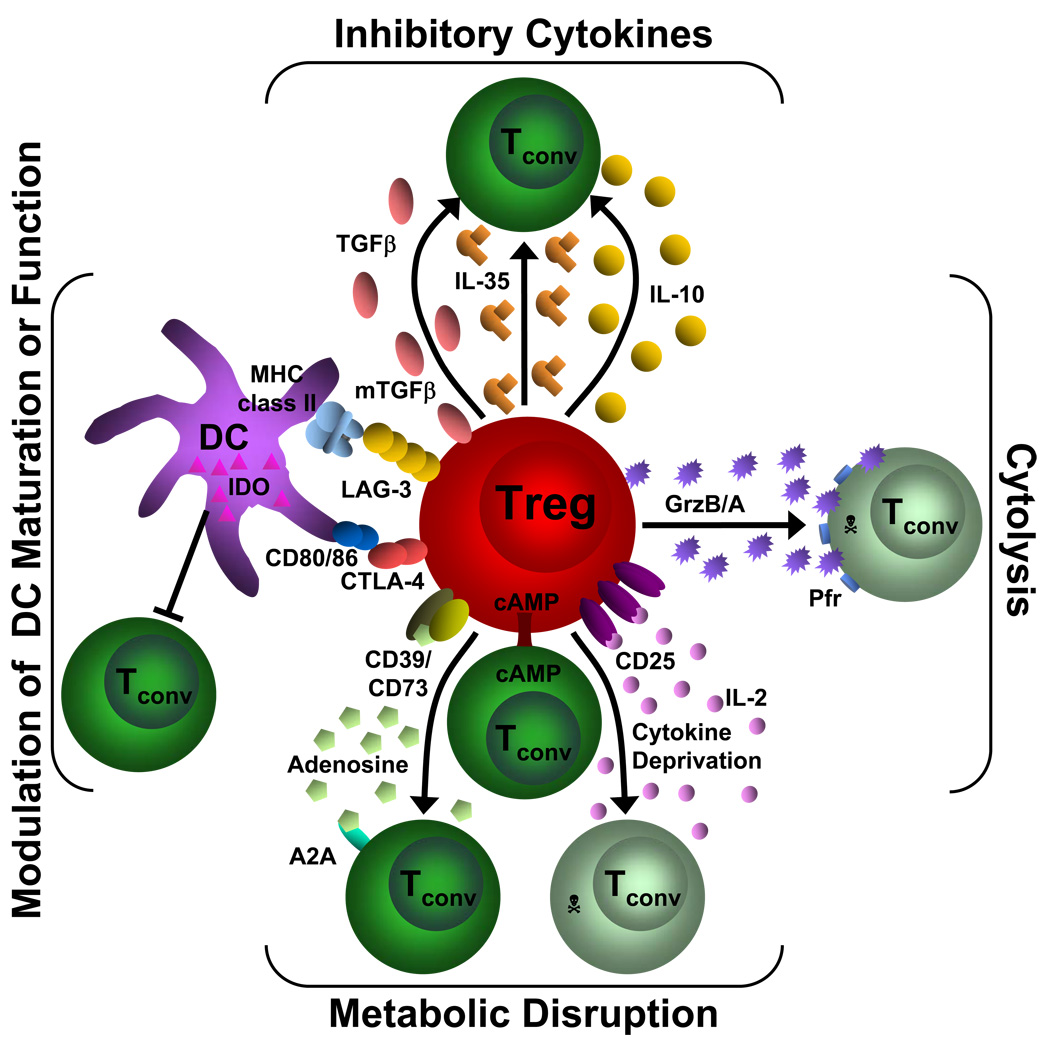
Figure 2. Mechanisms of Treg suppression.
This diagram depicts the four basic modes of Treg suppression. A primary mode of Treg suppression is mediated through the inhibitory cytokines IL-10, IL-35 and TGFβ. Tregs also induce cytolysis through granzyme A/B (GrzB/A) and perforin (Pfr). They can disrupt metabolic function by IL-2 deprivation which results in apoptosis, cAMP inhibition or by CD39/CD73- generated A2A-mediated immunosuppression. Tregs can also modulate DC maturation or function via a CD80/86 and CTLA-4 interaction or through a LAG-3 and MHC class II interaction. In addition, they can induce the upregulation of IDO in DCs. Tconv= conventional T cell; GrzB/A= granzyme B or A, Pfr= perforin, cAMP= cyclic adenosine monophosphate, A2A= adenosine-purinergic adenosine receptor, IDO= indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase, DC= dendritic cell