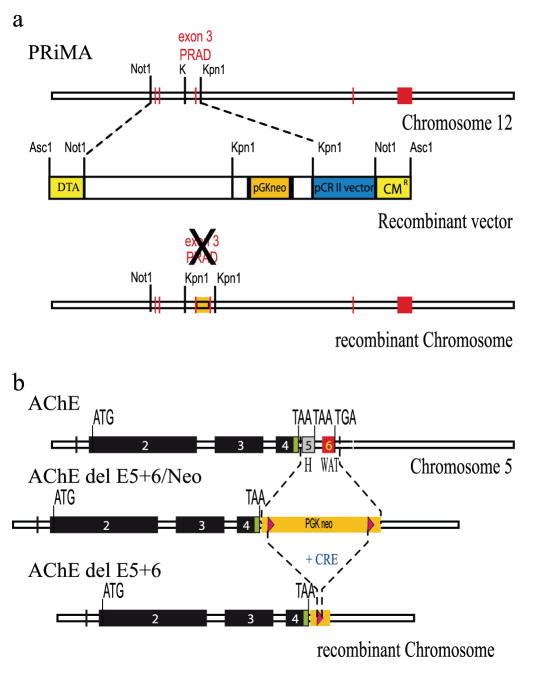
Figure 1. Generation of PRiMA and AChE del E5+6 knockout mice.
a) PRiMA (top): Map of the PRiMA gene in mouse chromosome 12. Exons are represented as red boxes. Exon 3 encodes the PRAD domain, the binding domain for AChE.
Recombinant vector (middle), with the restriction sites used for cloning. DTA, diphtheria toxin A (yellow). CM, chloramphenicol resistance (yellow). pGKneo, gene encoding neomycin resistance (orange box), Vector backbone (blue).
Map of the recombinant chromosome (bottom).
b) AChE (top): Map of the AChE gene in mouse chromosome 5. Exons encoding the catalytic domain are represented as black boxes (2-3-4) the alternative exons in grey (5) or red (6). Map of the recombinant chromosome after elimination of exons 5 and 6 (middle), showing the inserted gene encoding neomycin resistance (Camp et al., 2005).
Map of the recombinant chromosome after elimination of exons 5 and 6 and deletion of the resistance gene by Cre recombinase (bottom) (Camp et al., 2005).