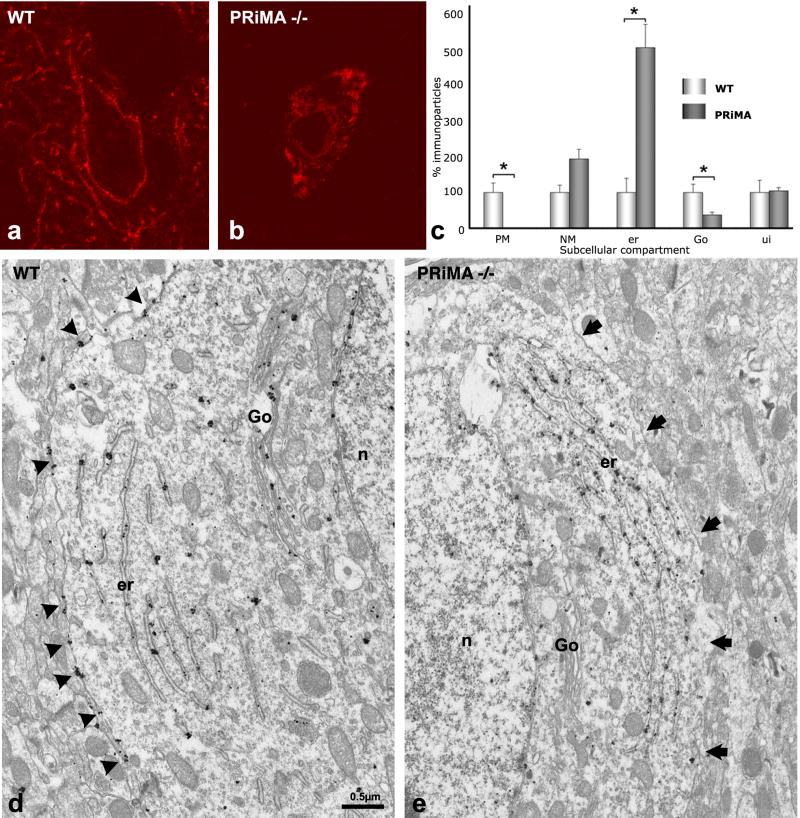
Figure 4. In the absence of PRiMA AChE accumulates in endoplasmic reticulum and is not found associated with the plasma membrane or the Golgi apparatus.
(a, b) Confocal microscopy reveals that AChE, detectable in the membranes of cell bodies and in axonal varicosities in the WT mouse, is found exclusively in the cytoplasm of the cell bodies of the PRiMA−/− knockout.
(c) Quantitative analysis of EM images (d, e). The number of immunoparticles associated with each compartment was counted and normalized to the length of the membrane in μm for the plasma membrane (PM) or the nuclear membrane (NM), or to the surface area in μm2 of the cytoplasm, the endoplasmic reticulum (er), or the unidentified compartment (ui). For Golgi apparatus (Go), values are expressed as the number of immunoparticles per Golgi apparatus. Data correspond to the analysis of 3 homozygous mice of each genotype, 10 neurons per animal. Results are expressed in relation to the 100 arbitrary unit value used for each WT control. In d, arrowheads point to immunoparticles associated with the plasma membrane. In e, arrows show the plasma membrane.