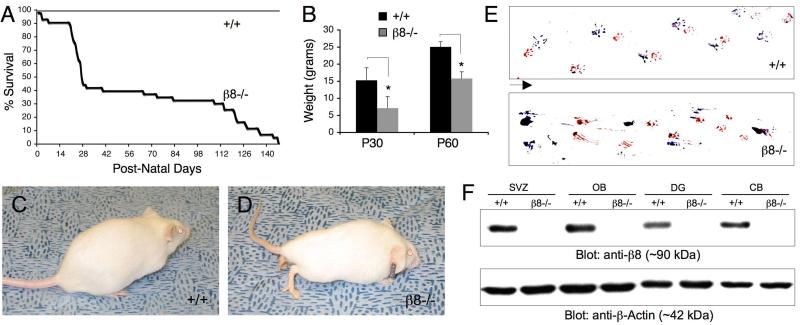
Figure 1. Genetic Background Influences Post-Natal Survival of β8-/- Mice.
(A); Kaplan-Meier survival plot using wild type (n=40) and β8-/- mice (n=39). Note that approximately 60% of β8-/- mice die by P30 whereas the remaining animals survive for up to five post-natal months. (B); Weight analysis using P30 and P60 control and mutant male mice (n=7 to 10 males per genotype, although similar results were observed with female mice). Note that β8-/- mice weigh significantly less compared to wild type littermates, *p < 0.0001 compared to wild type group (C, D); Images of four month-old (P120) wild type (C) and β8-/- (D) littermates. β8-/- mice display a hunched posture and limb paresis; these phenotypes develop with 100% penetrance in mutant mice that survive to adulthood. (E); Footprint analysis performed with post-natal day 90 (P90) wild type (upper panel) and β8-/- (lower panel) animals with hind paws painted blue and fore paws painted red. Note that the β8-/- mouse (like all other β8-/- mutants examined) displays an abnormal gait characterized by pronounced dragging of the limbs. Arrow indicates direction of movement. (F); Brain tissue homogenates were prepared from P60 wild type and β8-/- mice. Detergent-soluble protein lysates were immunoblotted with an anti-β8 integrin polyclonal antibody. Note that β8 integrin protein is expressed in the various brains regions of wild type mice, but is not detected in β8-/- animals. Abbreviations: SVZ, subventricular zone of lateral ventricle; OB, olfactory bulbs; DG, hippocampal dentate gyrus; CB, cerebellum.