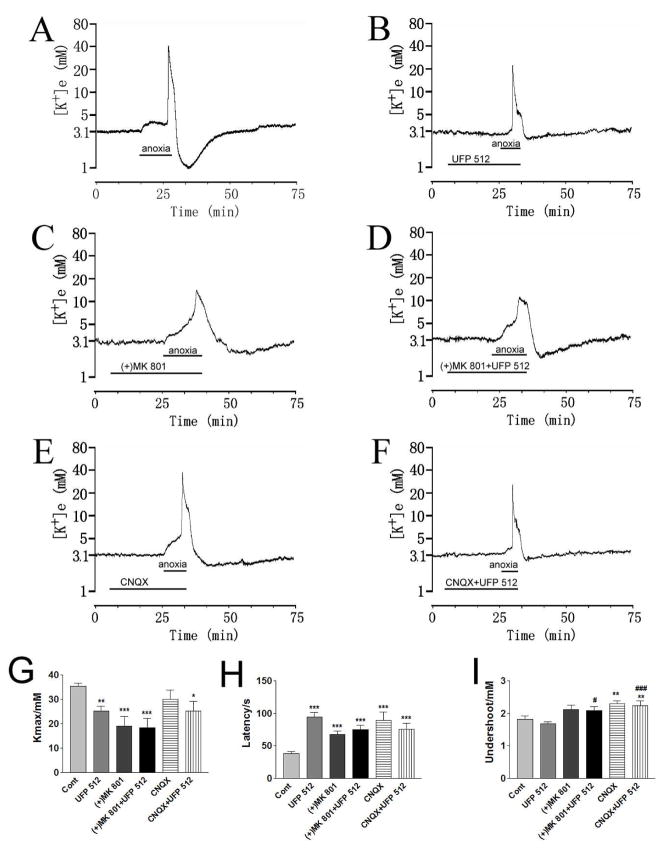
Fig. 3. Effect of ionotropic glutamate receptor blockers on the DOR protection from anoxic K+ derangement.
Trace recordings of A: Control (Cont), B: UFP 512 (1 μM), C: (+)MK 801 (10 μM), D: (+)MK 801+UFP 512, E: CNQX (10 μM), F: CNQX+UFP 512. G–I are statistical results of each recording parameter. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001 compared to controls; #p <0.05, ###p <0.001 compared to UFP 512-1.0. Note that (+)MK 801 (10 μM) significantly decreased anoxia-induced [K+]max (n=13), whereas CNQX (10 μM) only slightly decreased the anoxia-induced increase in peak [K+]e (n=12). Blockade of NMDA receptor channels with (+)MK 801 (10 μM) reduced DOR-induced protection from anoxic K+ derangement (n=13); In the presence of CNQX (10 μM), UFP 512 (1 μM) further attenuated the anoxia-induced increase in [K+]max (n=14).