Figure 6.
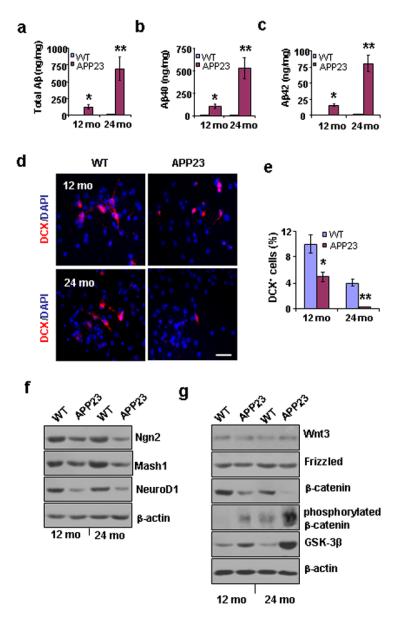
Aβ production, neurogenesis, proneural gene products, and β-catenin signaling in GPC progeny from APP23 vs. WT mice at 12 and 24 months of age. (a-c). Aβ ELISAs of neocortical samples from 12- and 24-month-old APP23 and WT mice revealed that total Aβ levels (a), Aβ40 levels (b), and Aβ42 levels (c) were significantly higher in the APP23 mice than in the WT mice, and the Aβ levels increased with age in the APP23 mice.(Student’s t test, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, n = 3 per group). (d). After 2 days in differentiation medium, immunostaining showed a reduced number of newborn neurons (DCX+) among the progeny of GPCs (labeled with DAPI) from APP23 mice at 12 and 24 months of age compared to age-matched WT mice. (e). Quantification of the immunoreactive structures revealed a significant reduction in the percentage of newborn neurons among the APP23 progeny compared to age-matched WT progeny (Student’s t test, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, n = 3 per group). (f). After 7 days in differentiation medium, the expression levels of the proneural gene products Ngn 2, Mash1, and neuroD1 were reduced in the GPC progeny from 12- and 24-month-old APP23 mice compared to those from age-matched WT mice (n = 3 per group). (g). After 7 days in differentiation medium, non-phosphorylated β-catenin levels decreased and both GSK-3β and phosphorylated β-catenin levels increased in the GPC progeny of 12 and 24-month-old APP23 mice compared to age-matched WT mice; however, no significant changes in the levels of Wnt3 or frizzled were observed (n = 3 per group). Scale bar represents 50 μm.
