Figure 8. Regulation of IFN responses in cells infected with SARS-CoV.
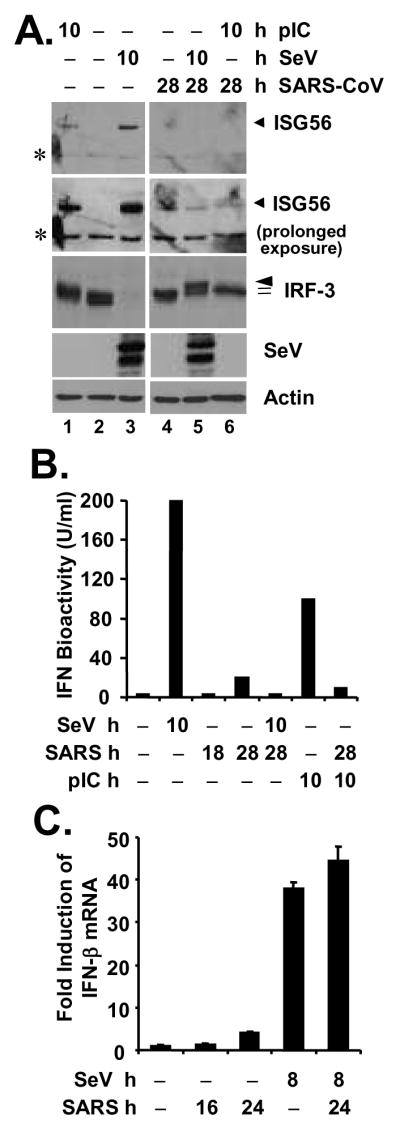
A. MA104 cells were mock-infected (lanes 1 through 3) or infected with SARS-CoV (MOI=10) for 18 h (lanes 4 through 6), followed by mock-treatment (lanes 2 and 4), transfection of poly (I-C) (lanes 1 and 6) or superinfection of SeV (lanes 3 and 5) for 10 h, respectively (a total of 28 h after mock or SARS-CoV infection under these conditions). Immunoblot analysis of cell lysates for expression of ISG56, IRF-3, SeV and actin is shown. Asterisks (*) in ISG56 panels denote a nonspecific band. B. MA104 cells were mock-infected, infected with SeV for 10 h, infected with SARS-CoV (MOI=10) for 18 or 28 h, or transfected with poly (I-C) for 10 h, respectively, or pre-infected with SARS-CoV for 18 h and then superinfected with SeV or transfected with poly (I-C) for additional 10 h (a total of 28 h after SARS-CoV infection under these conditions). Cell-free culture supernatants were collected, irradiated, and subjected to IFN bioactivity assay against VSV as described in Experimental Procedures. Bars indicate IFN bioactivity (U/ml) in culture supernatants under the indicated conditions. C. MA104 cells were mock-infected, infected with SeV for 8 h, infected with SARS-CoV (MOI=10) for 16 or 24 h, or pre-infected with SARS-CoV for 16 h and then superinfected with SeV for additional 8 h. Cells were harvested for total RNA extraction, cDNA synthesis, and subsequent real-time RT-PCR detection of IFN-β mRNA. Data shown are representative of two independently conducted experiments.
