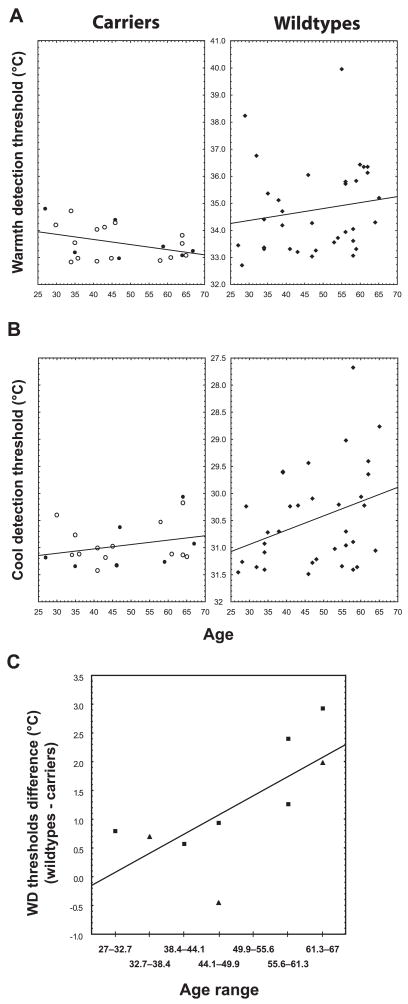
Figure 2.
Correlations with age. A, In the wild types (right), the correlation between WD thresholds and age was positive but not statistically significant (r =0.16, p =0.37). In the carriers (left), this correlation displayed a trend in the opposite direction (r =−0.39, p =0.08). These two correlations were statistically different, p =0.054. B, Cool detection thresholds increased with age in the wild types (r =0.34, p =0.05; right), but not in the carriers (r = 0.27, p =0.24; left). However, these correlations were not statistically different (p =0.82). See the Figure 1 legend for more information. C, The matched-pair analysis showed that the differences between the WD thresholds of the carriers and those of gender- and sex-matched wild types significantly increased with age (Spearman r =0.76, p =0.02). Squares, Male; triangles, female.