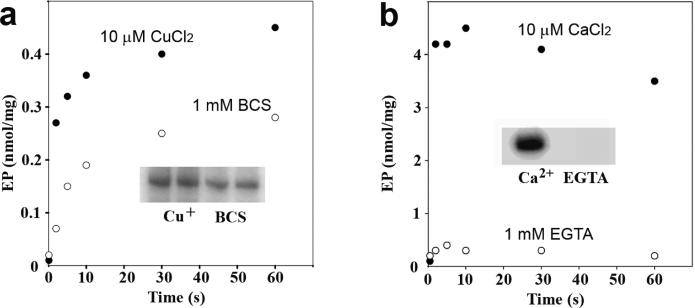
Figure 6.
Effect of copper or calcium on formation of the phosphoenzyme upon addition of ATP to A. fulgidus CopA or Ca2+ ATPase (SERCA1a). Specific cation dependence of phosphoenzyme formation by A. fulgidus CopA (a) and SERCA1a Ca2+ ATPase (b), to be compared with that of T. maritima CopA (shown in Figure 5). (a) The reaction was started by the addition of 25 μM [γ-32P]ATP to 25 μg/mL CopA in the presence of 3 μM CuCl2 (•) or in the absence (○) of copper (1 mM BCS present) at 60 °C. (b) The reaction was started by the addition of 25 μM [γ-32P]ATP to 25 μg/mL SERCA1a in the presence of 50 μM CaCl2 (•) or in the absence (○) of calcium (1 mM EGTA present) at 25 °C. Autoradiograms showing steady state levels of the radioactive phosphoenzyme are shown as insets.