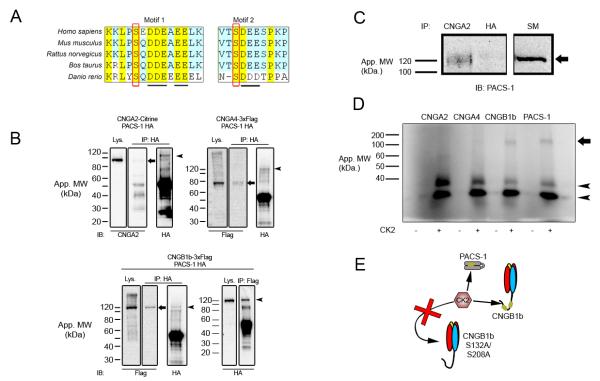
Figure 2. CNGB1b Contains Acidic Clusters, Interacts with PACS-1, and can Serve as a Substrate for CK2.
(A) Amino acid sequence alignment of the CNGB1b subunit from Homo sapiens, Mus musculus, Rattus norvegicus, Bos taurus, and Danio rerio. Acidic clusters marked by underline and putative CK2 phosphorylation sites marked by red rectangle. (B) Immunoprecipitation experiments from HEK293 cells cotransfected with HA-PACS-1 and either CNGA2-mCitrine (top left), CNGA4-3xFlag (top right), or CNGB1b-3xFlag (bottom). Immunoprecipitations were performed with either rabbit anti-HA (IP: HA; top left, top right, bottom left) or rabbit anti-flag (IP: Flag; bottom right) and blots were probed with mouse CNGA2 (IB: CNGA2), mouse anti-Flag M2 (IB: Flag), or rabbit anti-HA (IB: HA). Arrows mark CNGA2 (top left), CNGA4 (top right), and CNGB1b (bottom left). Arrowheads mark PACS-1. Lys. = lysates IP = Immunoprecipitation. (C) Immunoprecipitation experiment from adult CD1 mouse olfactory epithelial lysates. Immunoprecipitations of endogenous protein were performed either with anti-CNGA2 or negative control, anti-HA antibodies. Blot was probed with anti-PACS-1 antibodies. Arrow marks PACS-1 protein at approximately 120 kDa. SM = 10% starting material. (D) (Top) Autoradiograph from in vitro kinase reaction performed on immunoprecipitated proteins (CNGA2, CNGA4, CNGB1b, or PACS-1) in the presence (+) or absence (−) of recombinant CK2. Autophosphorylated CK2 bands marked with arrowheads. Arrow marks approximate molecular weight of PACS-1 and CNGB1b. (E) Model depicting predicted CK2-mediated phosphorylation of both PACS-1 and CNGB1b, but not CNGB1b S132A/S208A.