Figure 5. Inhibition of CK2 Activity Causes a Loss of CNG Channel Ciliary Localization.
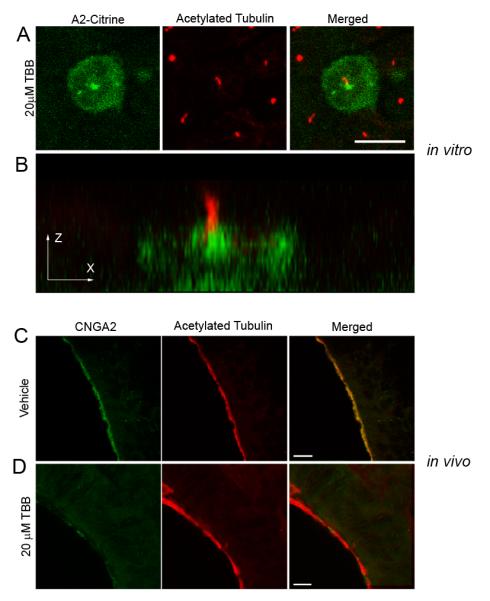
(A,B) MDCK cells were transfected with CNGA2-mCitrine and CNGB1b-3xFlag and allowed time for ciliary delivery followed by 4 hours of treatment with 20 μM of the CK2 inhibitor, TBB. (A) Compressed confocal image of a MDCK cell with CNGA2-mCitrine fluorescence shown in green and acetylated tubulin staining marking cilia shown in red. Bar represents 10 μm. (B) X-Z projection of the cell from panel A demonstrating concentration of CNG channel at base of cilium. (C, D) Representative compressed confocal stacks of coronal sections from OE from intranasally-injected CD1 mice. Confocal images of OE from adult CD1 mice treated with (C) DMSO vehicle or (D) 20 μM TBB for four hours. Signals shown are CNGA2 immunostaining (green, left), and acetylated tubulin immunostaining (red, middle). Merged images shown on right. Bars represent 10 μm.
