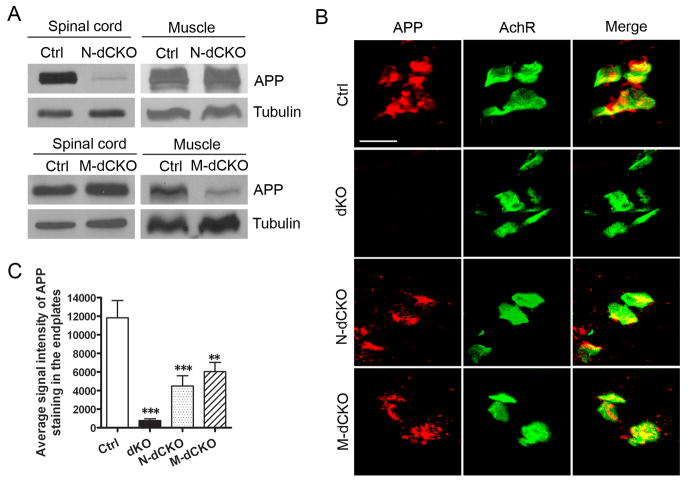
Figure 1.
Biochemical and immunohistochemical characterization of APP expression and localization. A. Western blot analysis of APP protein levels from P0 spinal cord or muscle samples of APLP2 null control (Ctrl), neuronal or muscle conditional APP knockout on APLP2 null background (N-dCKO and M-dCKO respectively) using the APPc antibody. Tubulin was used as a loading control. B. Immunofluorescence staining of P0 diaphragm muscle sections of control (Ctrl), APP/APLP2 double knockout (dKO), N-dCKO or M-dCKO animals using the anti-APP antibody Y188. α-bungarotoxin (α-BTX) staining was used to mark the postsynaptic acetylcholine receptors (AchR). Merge: overlay of APP and AchR images. Scale bar: 20 μM. C. Quantification of APP signal intensity (mean ± SEM, 2 animals/genotype, 6 sections/animal) in AchR-positive endplates. ***p<0.001, **p<0.01, as compared to control (one way ANOVA).