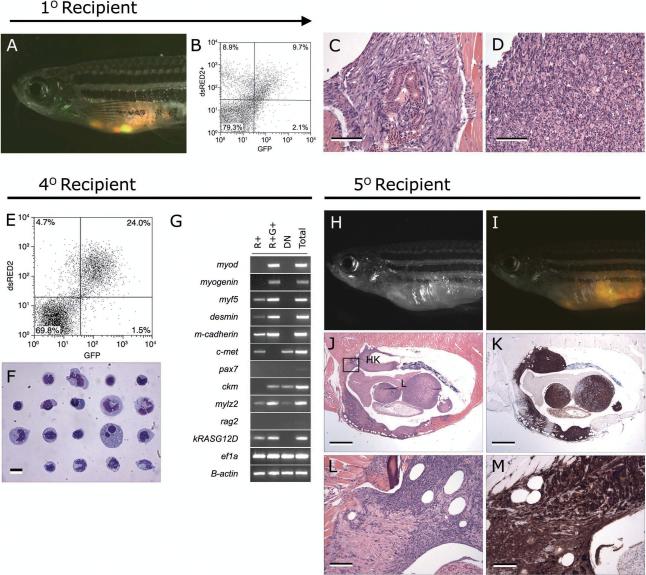
Figure 4.
The dsRED2+ cell population from double transgenic rag2-dsRED2/alpha-actin-GFP animals contains the serially transplantable cancer stem cell in zebrafish embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma. (A-D) Primary transplanted tumors from alpha-actin-GFP+/rag2-dsRED2+ fish (1O Recipient). (A) Merged image of GFP fluorescent, dsRED2 fluorescent, and bright field images. (B) FACS analysis of primary recipient engrafted with ERMS. (C-D) Histological analysis revealed heterogeneity in transplant animals, with some fish having masses of spindled cells (C) or round cell aggregates (D), or both. Scale bars equal 100 microns in C-D. (E-G) Cells isolated from serially transplanted animals, in this case a quaternary recipient animal (4O Recipient). (E) FACS plot of tumor cells isolated from a 4O recipient. (F) Wright-Giemsa stained cytospins of FACS sorted R+ cells from quaternary tumor. (G) Semi-quantitative RT-PCR analysis of FACS sorted cell populations. Total refers to total cells isolated from quaternary transplanted RMS isolated by FACS based on cell-viability and serve as an input control. (H-M) Fish transplanted with 50 R+ cells defined in panels E-G (5O Recipient). (H) Brightfield image of transplant recipient animal. (I) Merged image of a dsRED2+/GFP+ tumor in same animal. (J) Hematoxylin and eosin stained and (K) anti-GFP immunostained section of transplanted fish showing that RMS cells infiltrate the liver (L), head kidney (HK), and skeletal muscle. (L-M) High power magnification of boxed region in J. Scale bar equals 1mm (J-K) and 100 microns (L-M). (Modified from Langenau et al., 2007).