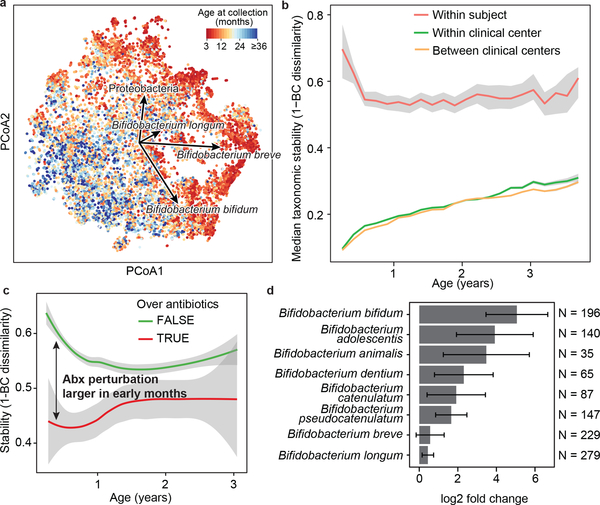
Figure 2: The early gut microbiome is characterized by early Bifidobacterium species heterogeneity and individualized accrual of taxa over time.
a, PCoA ordination of microbial beta diversities (N = 10,913 samples), measured by Bray-Curtis dissimilarity. Arrows show weighted averages of key taxonomic groups. b, Microbiota stability, measured by Bray-Curtis (BC) dissimilarity (N = 10,750 samples) in three-month time windows, over two-month increments, stratified in three groups: within subject, within clinical center, and between clinical centers. Lines show median per time window. Shaded area shows estimated 99% confidence interval. Gut microbial communities were highly individual. c, Influence of antibiotic courses on microbial stability, measured by Bray-Curtis dissimilarity over consecutive stool samples (<50 days apart) from the same individual during the first three years of life and stratified by whether antibiotics were given between the two samples (N = 654 observations with antibiotics, N = 6,734 observations without antibiotics). Curves show locally weighted scatterplot smoothing (LOESS) for the data per category. Shaded areas show permutation-based 95% confidence intervals for the fit. d, Decreases in the most common Bifidobacterium species in connection to oral antibiotic treatments. Fold change was measured between consecutive samples with an antibiotic course between them, given that the species in question was present in the first of the two samples. Sample size per species (N) indicates the number of sample pairs where the species in question was present in the sample preceding the antibiotic treatment. Bars show bootstrapped log2 fold change decrease (mean and standard deviation, N = 1,000 bootstrap samples).