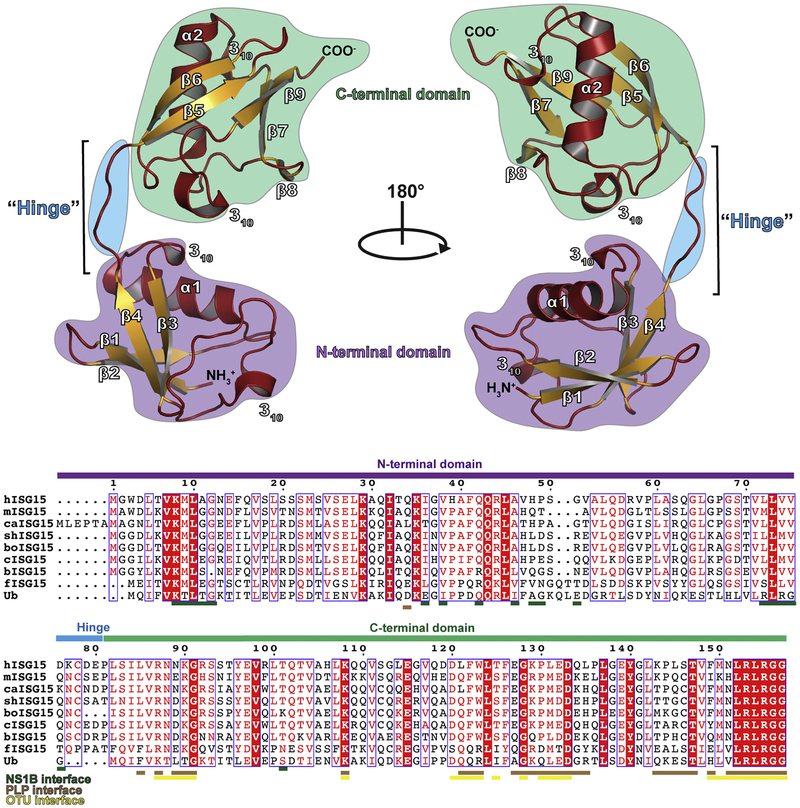
Figure 2:
Structure of human ISG15 (PDB entry 1Z2M). The secondary structure is denoted with helices and loops shown in red and sheets shown in gold. The C-terminal domain is denoted by a green background, hinge region by a blue background, and the N-terminal domain by a purple background. A sequence alignment of human ISG15 (hISG15), mouse ISG15 (mISG15), canine ISG15 (caISG15), sheep ISG15 (shISG15), bovine ISG15 (boISG15), camel ISG15 (cISG15), vesper bat ISG15 (bISG15), fish ISG15 (fISG15), and ubiquitin (Ub) is shown with the domain architecture indicated with colored bars. The residues of ISG15 known to interact with the influenza B NS1 protein, coronavirus papain-like proteases (PLPs), and nairovirus ovarian tumor domain proteases (OTUs) are indicated. The sequence alignment graphic was generated using the ESPript server [83].