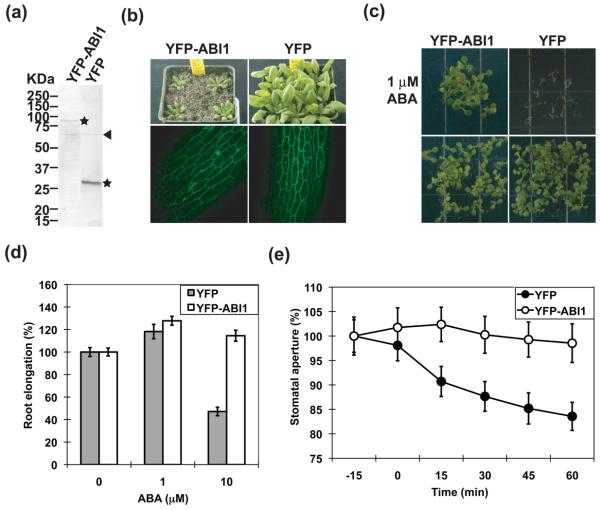
Figure 1. Constitutive expression of YFP-ABI1 causes ABA insensitivity.
(a) Western blot analysis of YFP-tagged ABI1 (left) and YFP control (right) proteins in transgenic Arabidopsis. Stars indicate predicted YFP-ABI1 and YFP bands. Arrow head: nonspecific band. (b) Morphology and subcellular localization of Arabidopsis plants constitutively expressing YFP-ABI1 (left) and YFP (right) at the rosette plant stage. Plants were grown for 5 weeks in soil. (c) ABA-insensitive phenotype of constitutively-expressed YFP-ABI1 (left) and ABA response in control YFP-expressing seedlings (right). Top: in the presence of 1 μM ABA. Bottom: without added ABA. Transgenic plant seeds were sown on agar MS plates with or without 1 μM exogenous ABA. (d) ABA-dependent root growth responses of Arabidopsis seedlings constitutively expressing YFP and YFP-ABI1. Seedlings were germinated and grown on hormone-free MS plates for 5 d and then transferred to MS plates containing the indicated ABA concentrations. Root length was measured 4 d after transfer. Error bars show standard deviations. (e) Time course experiments of ABA-induced stomatal closing in YFP control and YFP-ABI1 expressing leaves (genotype blind experiments). Stomatal apertures were individually mapped and images captured (Siegel et al. 2009) and measured before and after addition of 1 μM ABA. Average stomatal apertures at time=−15 min: 3.47 ± 0.14 μm (YFP plants), 3.75 ± 0.18 μm (YFP-ABI1 plants). YFP plants: n=23 stomata, YFP-ABI1 plants: n=26 stomata. Error bars show SEM.