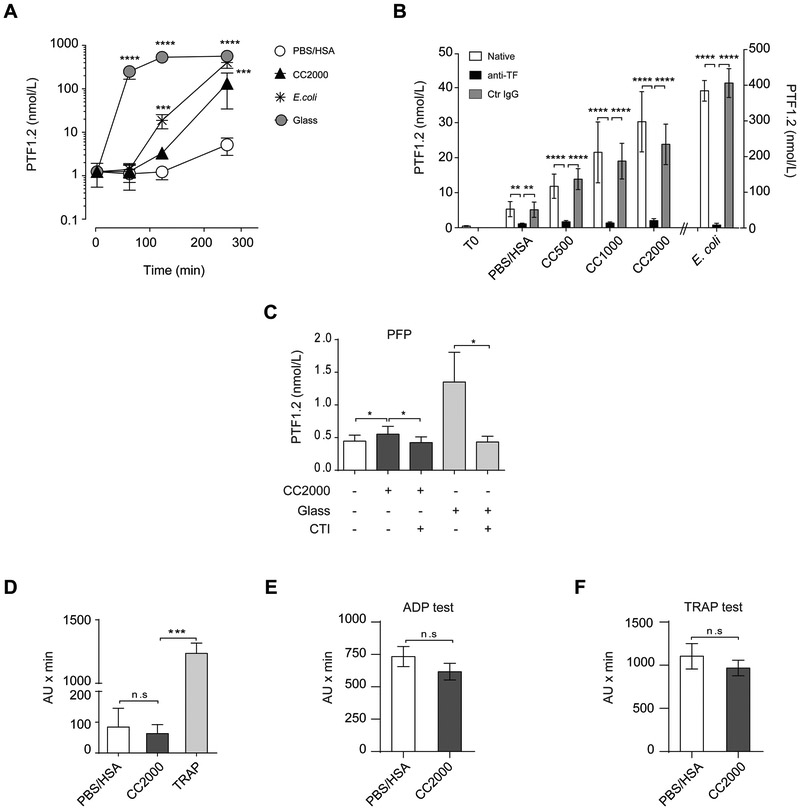
Figure 2. Cholesterol crystals (CC) induce prothrombin fragment factor 1+2 (PTF1.2) dependent on the tissue factor pathway.
(A) PTF1.2 induction over time (60, 120 and 240 min) upon exposure to CC 2000 μg/mL, PBS/HSA, E. coli (1 × 107 particles/mL) or glass (N=7 donors) in human whole blood. (B) Effect of TF inhibition following exposure of CC (500, 1000 and 2000 μg/mL) or E.coli after addition of the functional grade inhibitory antibody against TF (anti-TF) or the corresponding ultra-leaf purified IgG1κ control antibody (Ctr IgG) for 240 min in human whole blood (N=6 donors). (C) Effect of factor XII inhibition by CTI (40 μg/mL) in platelets reduced plasma (PFP) following incubation with CC (2000 μg/mL) or glass for 60 min (N=5). Effect of CC on platelet aggregation in human whole blood measured by electrical impedance aggregometry in (D) by CC (2000 μg/mL) or its controls HSA/PBS or thrombin receptor activating peptide-6 (TRAP) (N=6), (E) by additional stimulation with ADP (N=3) and in (F) with TRAP following 6 min incubation (N=3) given as arbitrary units × min. Under all experiments thrombin was inhibited with lepirudin. All data are given as means ± SEM. The statistical differences are given by the following significance levels *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001.