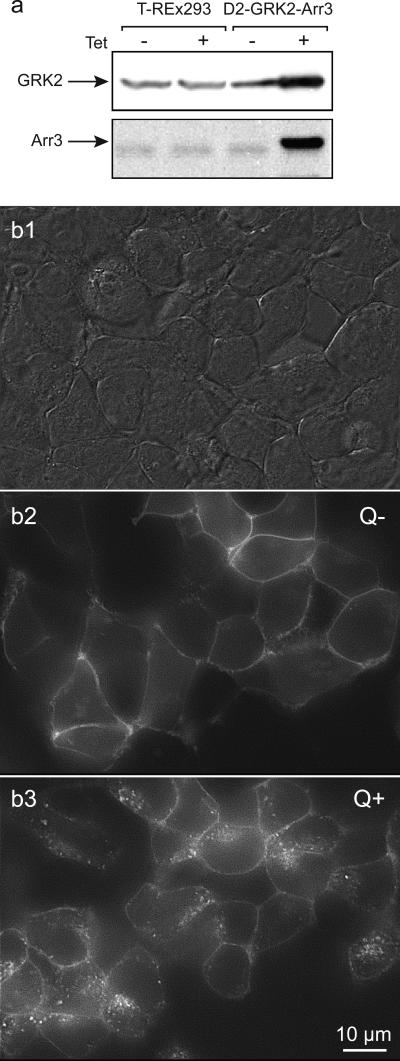
Figure 1. Visualization of GRK2 and arrestin3 enhanced quinpirole-induced D2 receptor internalization.
T-REx-293 cells were triple transfected with D2 receptors, with the FLAG epitope on the extracellular N-terminus and yellow-fluorescent protein (YFP) on the intracellular C-terminus of D2 receptors, GRK2 and arrestin3 (Arr3). a. Immunoblot analysis of preparations from T-REx-293 control and D2-GRK2-Arr3 triple-transfected cells. Tetracycline had no effect on basal expression of GRK2 and arrestin3 in control T-REx-293 cells (left), while it induced robust expression of GRK2 and arrestin3 in the triple-transfected cells. GRK2 and arrestin3 proteins were detected by polyclonal anti-GRK2 and anti-arrestin3 antibodies, respectively. b. Cells were treated with tetracycline and then viewed under DIC optics (b1) or epic-fluorescence (b2), and then again following quinpirole treatment (b3). Under control condition (Q−), D2 receptors were mainly expressed at the cell surface, as indicated by the surface fluorescence labeling of Zenon anti-FLAG and D2 receptor-YFP fluorescence (b2). Quinpirole (Q+) induced a dramatic redistribution of EYFP fluorescence into a punctate intracellular pattern, reflecting robust D2 receptor internalization (b3). Cells have shifted shape and position during the quinpirole incubation so the images are not directly super imposable.