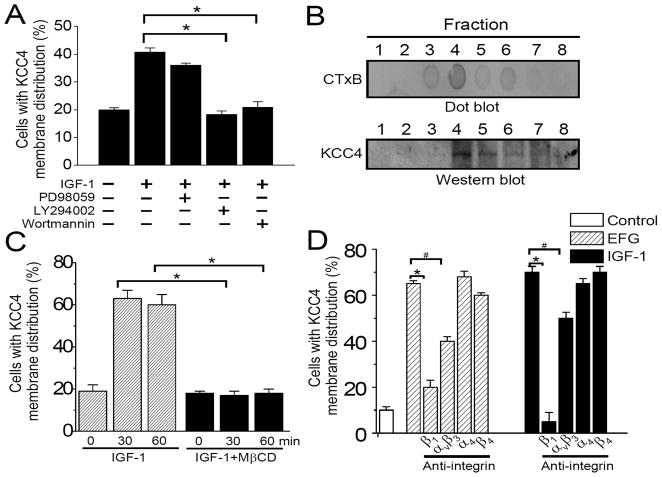
Figure 3. The regulatory mechanisms of KCC4 recruitment.
(A) Signals regulating KCC4 surface expression. OVCAR-3 cells were pre-incubated with different inhibitors (20 μM LY294002, 100 nM wortmannin or 50 μM PD98059) for 30 min and then exposed to IGF-1 (100 ng/ml) stimulation for 30 min. The confocal imaging analyses were performed after immunofluorescent staining with KCC4. (B) KCC4 mainly distributes in the fractions of lipid rafts after IGF-1 stimulation. Lipid rafts were isolated as described in Materials and Methods. CT×B: cholera toxin subunit B, the lipid raft marker. (C) Lipid rafts are necessary for KCC4 membrane trafficking. OVCAR-3 cells were pre-incubated without or with MβCD (10 mM) for 30 min to disrupt lipid rafts prior to IGF-1 stimulation. (D) Integrin signaling is involved in KCC4 recruitment. Before IGF-1 or EGF stimulation, OVCAR-3 cells were pretreated with different functional-blocking monoclonal antibodies (15 μg/ml) against integrin for 30 min. Each column in (C) & (D) represents mean ± S.E.M. of at least 150 cells. #P<0.05; *P<0.01 by unpaired t test.