Figure 2.
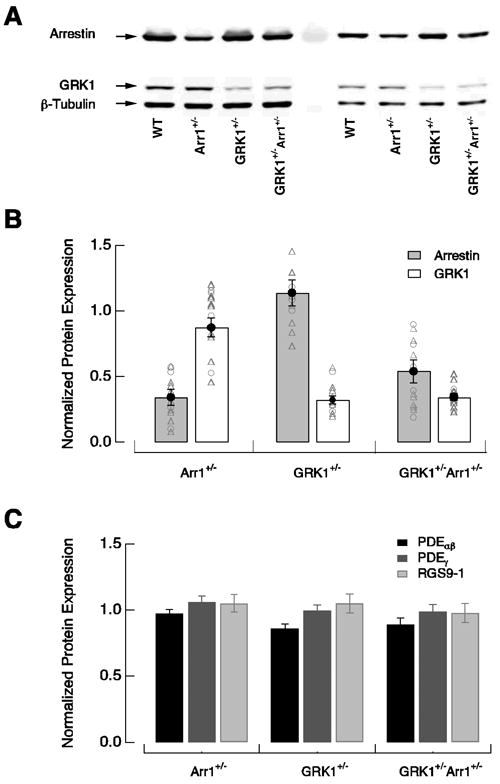
Protein expression in wild-type, Arr1+/−, GRK1+/−, and GRK1+/−Arr1+/− rods. (A) Representative immublot analysis of arrestin and GRK1 expression in retinas of wild-type and heterozygous knockout mice. The blot was probed with polyclonal anti-arrestin, monoclonal anti-rhododopsin kinase 1a, and monoclonal anti-β tubulin antibodies. Two different dilutions of the same samples were run on the same blot. (B) Levels of arrestin1 and GRK1 expression in heterozygous knockout retinas normalized to the levels in wild-type retinas. Integrated fluorescence intensity values were used for all analyses. Variations in sample loading were corrected for by normalizing the intensity value of each protein band to the intensity value of β-tubulin in the same lane. Open circles and triangles show the results from two different dilutions. Normalized ratios of arrestin1 and GRK1 expression compared to wild-type values for Arr1+/− were 0.34 ± 0.06 and 0.87 ± 0.07 (mean ± SEM, n = 5); 1.14 ± 0.10 and 0.32 ± 0.03 for GRK1+/− (n = 4); and 0.54 ± 0.09 and 0.34 ± 0.03 for GRK1+/−Arr1+/− (n = 5). (C) Levels of PDEαβ, PDEγ and RGS9-1 expression in heterozygous retinas normalized to the levels in wild-type retinas. Normalized ratios of PDEαβ, PDEγ and RGS9-1 compared to wild-type values for Arr1+/− were 0.97 ± 0.03, 1.06 ± 0.05, and 1.05 ± 0.07 (n = 4); 0.86 ± 0.03, 0.99 ± 0.04, and 1.05 ± 0.07 for GRK1+/− (n = 4); 0.89 ± 0.05, 0.99 ± 0.05, and 0.98 ± 0.07 for GRK1+/−Arr1+/− (n = 4).
