Figure 5. Ca2+-dependent and independent change in Egly.
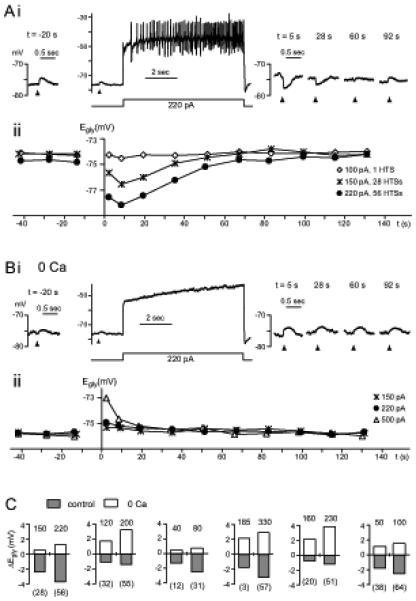
(A,B) Data from one cell comparing glycine responses and Egly measurements in control condition (A) with those in zero-Ca2+ (B). Time 0 is the moment the 8-sec depolarizing current injection terminated. (Ai) After 56 high-threshold Ca2+ spikes induced with a 220 pA injection, the glycine response shifted negative. (Aii) The Egly series measured along with the Vm recording in (Ai) is shown (?) with two other series obtained with different amount of current injections. The negative Egly shifts peaked at 8.5 sec. HTSs: high threshold spikes. (Bi,ii) The Vm and Egly series in zero-Ca2+ (replaced with Mg2+) are displayed in the same way as in (A). After a depolarization in zero-Ca2+, no negative shift but a positive shift in Egly occurred. Bias current was −40 pA in (Ai) and −55 pA in (Bi). (C) Bar graphs showing the peak change in Egly after an 8-sec current injection (amount in pA indicated above each bar) in control condition and in zero-Ca2+, from 6 cells. Number of Ca2+ spikes evoked is shown in parentheses under each bar belonging to control conditions. All data were obtained in TTX.
