Fig. 2. Increased protein expression of death receptor signaling in the hippocampal dentate gyrus (DG) of post-mortem AUD human brain.
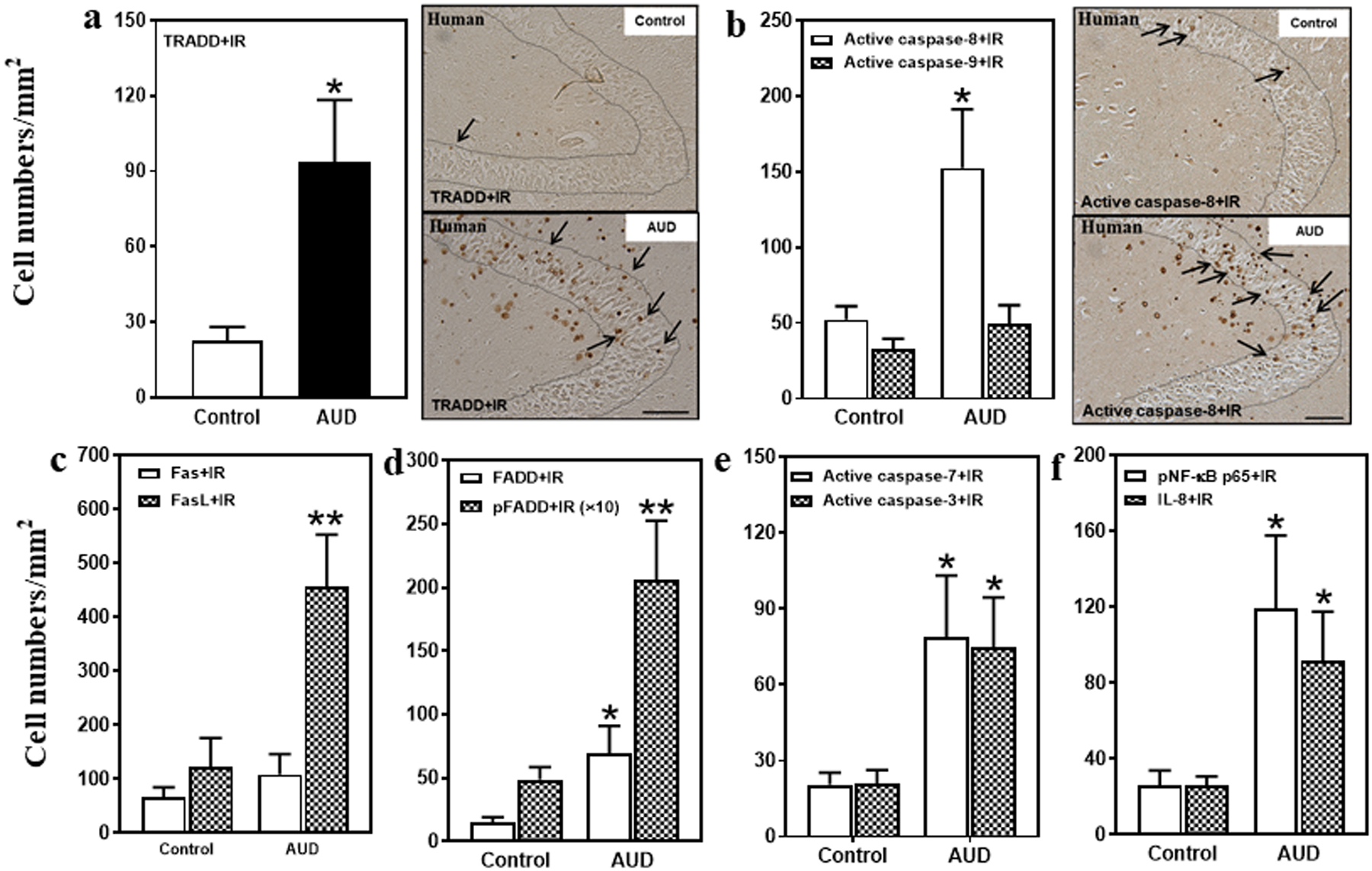
(a) Left side: TRADD+IR expression was significantly increased (407% of control) in the AUD DG. Right panel: TRADD+IR expression in the DG of post-mortem human hippocampus (immunohistochemical staining, bar scale = 50 μm). (b) Right side: Active caspase-8+IR expression was increased (292% of control), but there was no change in active caspase-9+IR expression in the AUD DG. Right panel: Active caspase-8+IR expression in the DG of post-mortem human hippocampus (immunohistochemical staining, bar scale = 50 μm). (c) FasL+IR expression was significantly increased (370% of control) in the AUD DG. However, there was not significant change in Fas+IR expression. (d) FADD+IR (469% of control) and pFADD+IR (424% of control) expression were significantly increased in the AUD DG. (e) Active caspase-7+IR (385% of control) and active caspase-3+IR (356% of control) expression were significantly increased in the AUD DG. (f) pNF-κB p65+IR (342% of control) and IL-8+IR (347% of control) expression were significantly increased in the AUD DG. Data are expressed as the numbers of cells. Each point is mean ± SEM per mm2 (n = 9–10/group). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 compared with control group with Independent Samples T-Test.
