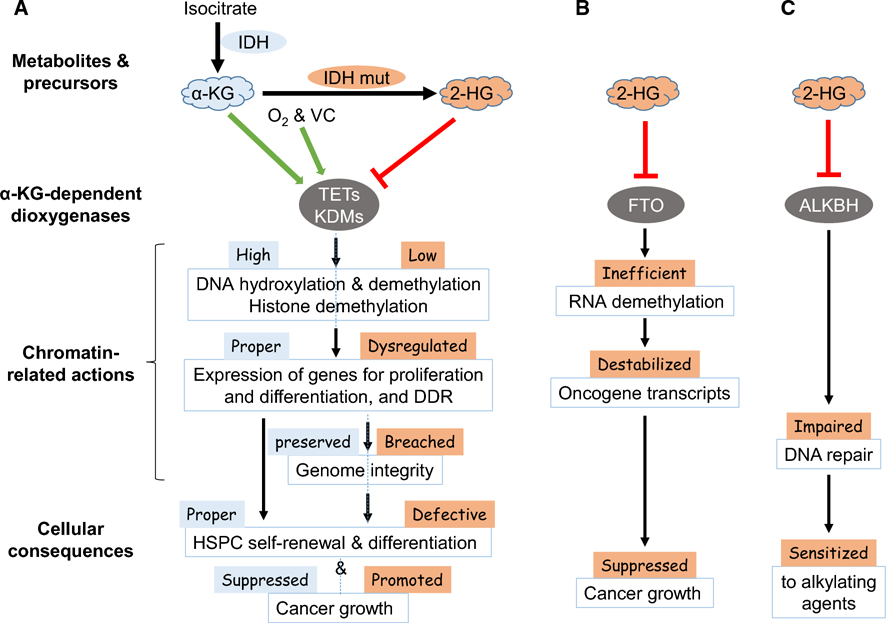
Figure 2. Different chromatin regulation of cell functions by the metabolites from Isocitrate.
α-KG is generated from isocitrate by IDH, and serves as an essential cofactor for a large number of α-KG-dependent dioxygenases including those shown here. These enzymes exert different molecular activities on chromatin (A), RNA modifications (B), and DNA repair proteins (C), which affect gene expression and DDR to ensure proper gene expression and preserve genome integrity for normal hematopoietic cell fate determination and function. In contrast, 2-HG is generated from α-KG by IDH mutants frequently found in cancer, and inhibits these α-KG-dependent dioxygenases and affect the different activities on chromatin (A), RNA (B), and DNA repair (C), and eventually lead to aberrant hematopoietic fate determination and different outcome of cancer growth.