Figure 6. Manipulation of β-catenin signaling alters the axonal projection patterns of electroporated cortical neurons.
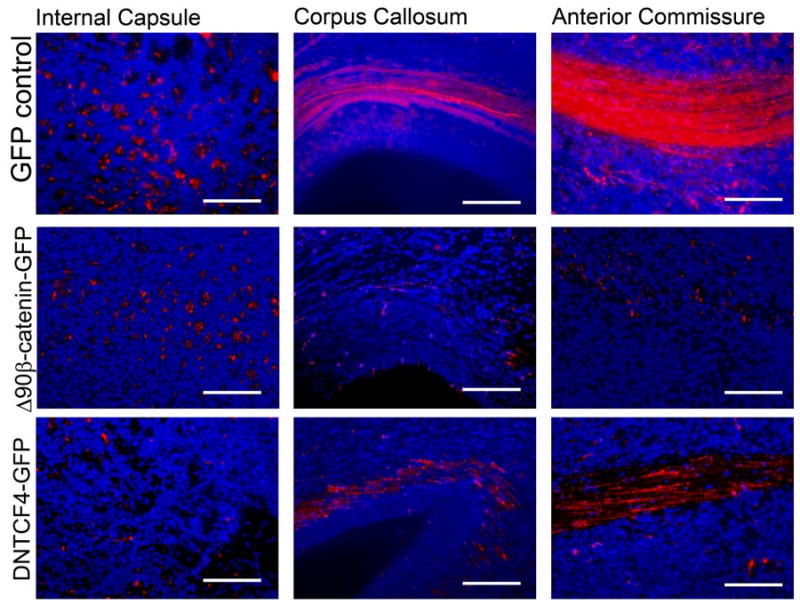
E13.5 embryos electroporated with pCAG-mCherry and either pCAG-GFP, pCAG-Δ90β-cateninGFP, or pCAG-dnTCFGFP, and axonal projection patterns analyzed at E19.5. Coronal sections through the level of the anterior commissure were produced for all three groups. At this section level, both corticocortial projection pathways (through the corpus callosum and the anterior commissure) and subcortical projection pathways (through the internal capsule whose fibers are perpendicular to the plain of the section) are visible. Cells co-electroporated with GFP control plasmid and mCherry projected many mCherry-positive processes through both subcortical (internal capsule) and corticocortical (anterior commissure and corpus callosum) projection pathways. Cells electroporated with Δ90β-cateninGFP exhibit many mCherry-positive processes through the internal capsule, but few through the corpus callosum or the anterior commissure. Meanwhile, cortical cells electroporated with dnTCF4GFP have very few mCherry-positive processes in the internal capsule, but numerous mCherry-positive processes through the anterior commissure and corpus callosum. mCherry staining pseudocolored red and DNA pseudocolored blue. Bars = 125 μm in high power images.
