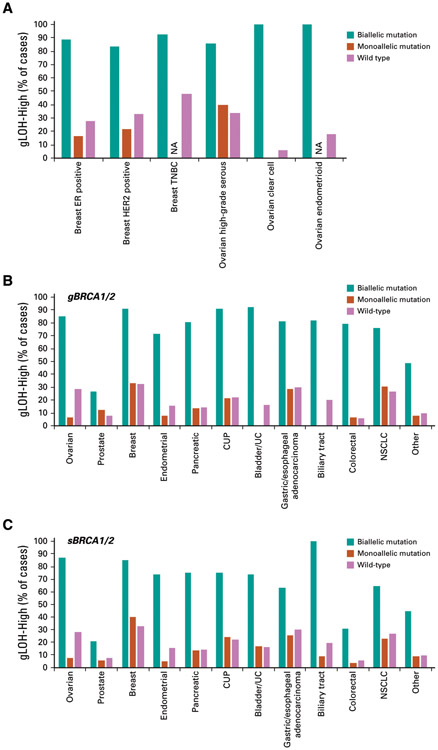
FIG A6.
(A) The frequency of BRCA1/2 biallelic, monoallelic, and wild-type cases that were high genome-wide loss of heterozygosity (gLOH-high) was compared in the subset of ovarian and breast cancer cases where molecular/histologic subtype information was available (see Data Supplement). (B) Frequency of predicted germline BRCA1/2 (gBRCA1/2) biallelic, monoallelic, and wild-type cases that were gLOH-high (see Data Supplement). (C) Frequency of predicted somatic BRCA1/2 (sBRCA1/2) biallelic, monoallelic, and wild-type cases that were gLOH-high (see Data Supplement). CUP, cancer of unknown primary; ER, estrogen receptor; HER2, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2; NA, not available (no assessable alterations); NSCLC, non–small-cell lung cancer; TNBC, triple-negative breast cancer; UC, urothelial cancer.