Figure 1.
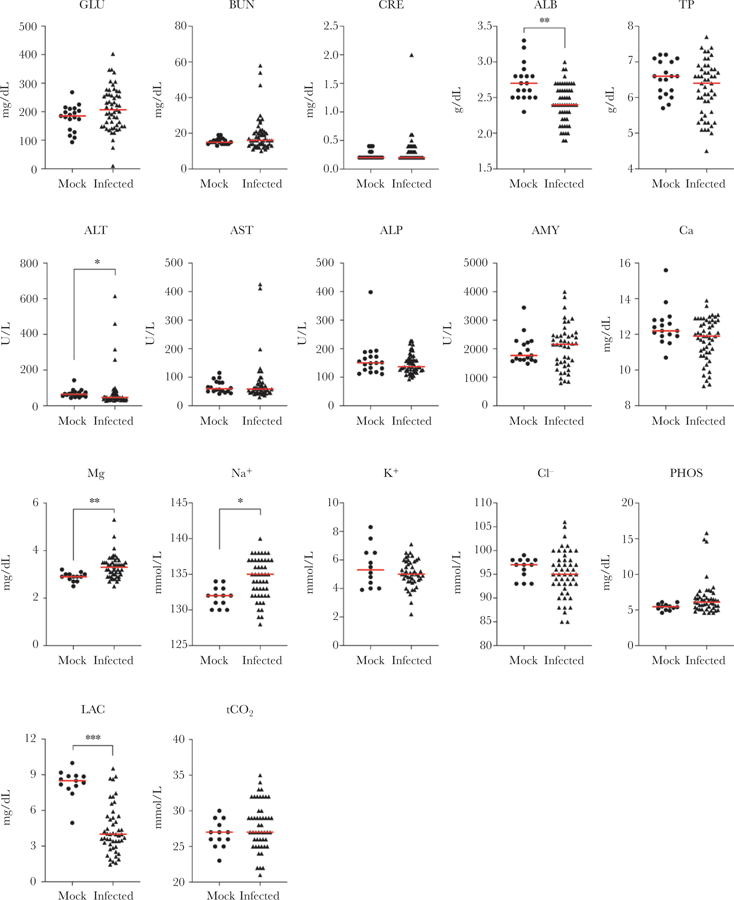
Alterations in blood chemistry in terminal Nipah virus (NiV)-infected animals. Age-matched female Syrian hamsters were mock-infected (Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium only, circles; n = 13 for Metlac 12 analytes or n = 19 for General Chemistry 13 analytes) or infected with Nipah virus (NiV)-Malaysia (n = 49–55, triangles). Samples from mock-infected controls and NiV-infected animals that were euthanized due to severe disease, regardless of route (intranasal or intraperitoneal), dose (103–107 TCID50 [50% tissue culture infective dose]), or virus stock (wild-type or recombinant), were analyzed using the Piccolo General Chemistry 13 (plasma) or Metlac 12 (whole blood) reagent discs. Individual values and median (red bar) are depicted..*, P < .01; **, P < .001; ***, P < .0001. ALB, albumin; ALP, alkaline phosphatase; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; AMY, amylase; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; BUN, blood urea nitrogen; Ca, total calcium; Cl−, chloride; CRE, creatinine; GLU, blood glucose; K+, potassium; LAC, lactate; Mg, magnesium; Na+, sodium; PHOS, phosphorus; tCO2, total carbon dioxide; TP, total protein.
