Figure. The counter-regulatory role of ACE2 in the renin-angiotensin system.
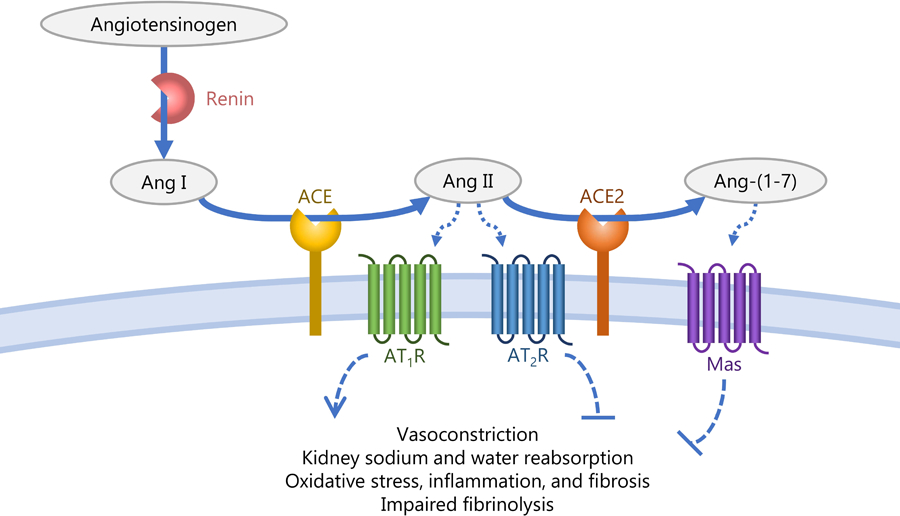
This figure demonstrates the conversion of angiotensinogen to Ang I by renin, Ang I to Ang II by ACE, and Ang II to Ang-(1–7) by ACE2. Ang II acts on the AT1R receptor to increase vasoconstriction, fluid and sodium retention by the kidney, and oxidative stress, resulting in increased blood pressure. Ang-(1–7) acts on the Mas receptor resulting in vasodilation, increased fluid and sodium excretion by the kidney, and a reduction in oxidative stress, resulting in reduced blood pressure.
