Figure 3.
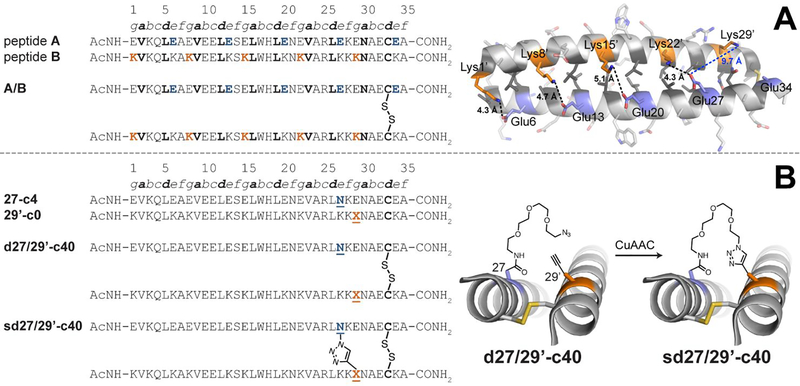
(A) Sequences of acidic peptide A and basic peptide B, along with disulfide-bonded parallel coiled-coil monomer A/B. Ribbon diagram of the published crystal structure of A/B (PDB ID: 1KD9), with side chains shown as sticks. e-position Glu residues on peptide A are colored blue; g-position Lys residues on peptide B are colored orange; non-polar a- and d-position residues on peptides A and B are colored dark grey. Black dotted lines indicate distances between the Oε2 of Glu and Nζ of Lys within each of four e/g’ interhelical salt bridges (i.e., Glu6/Lys1’, Glu13/Lys8’, Glu20/Lys15’, and Glu27/Lys22’). The blue dotted line indicates the distance between Oε2 of Glu27 and Nζ of Lys29’, which are not involved in an interhelical salt bridge with each other (B) Sequences of acidic variant 27-c4, basic variant 29’-c0, disulfide-bound coiled-coil monomer d27/29’-c40, and its triazole-stapled counterpart sd27/29’-c40. X represents propargyl glycine and N represents an azide-terminated Asn-PEG, with the structures as shown.