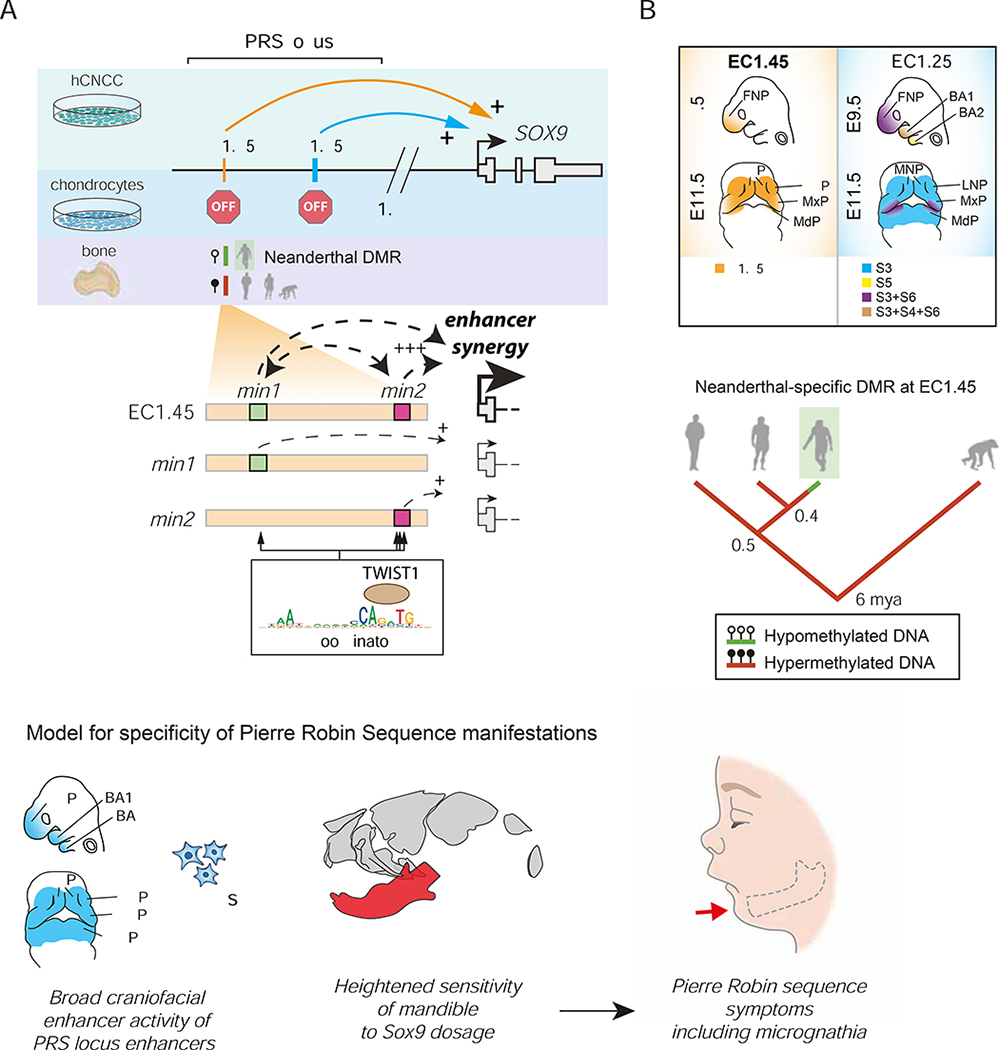
Figure 7: Summary of PRS locus enhancer activity, with a proposed model for PRS aetiology and associated Neanderthal DMR evolution.
(A) A model of EC1.45 and EC1.25 hCNCC-specific regulation of SOX9 expression at extreme long-distance followed by decommissioning in chondrocytes. A Neanderthal-specific hypomethylated region (HMR) overlaps EC1.45. Two minimal elements in EC1.45 have synergistic activity, i.e. (min1+min2) > (min1)+(min2). Coordinator motifs in min1 and min2 sequences are central for their activity and are bound by TWIST1.
(B) EC1.45 and EC1.25 are active in the developing face.
(C) A model for PRS aetiology, whereby by two features converge to confine disease phenotypes to the lower jaw.
(D) Phylogenetic tree of the inferred regulatory evolution for an EC1.45 Neanderthal-specific hypomethylated region (HMR, green). From left to right: anatomically modern humans (AMH), Denisovans, Neanderthals and chimpanzee. Million years ago, mya.
BA1–2, branchial arch 1–2; FNP, frontonasal prominence; LNP, lateral nasal process; MdP, mandibular process; MNP, medial nasal process; MxP, maxillary process. </p/> See also Figure S6.