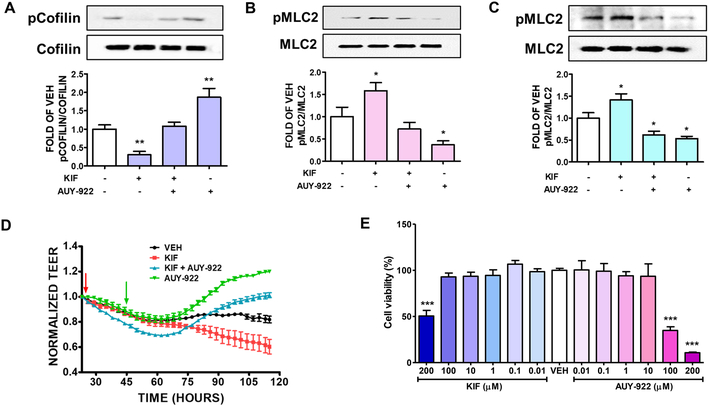
Figure 1: Effects of KIF and AUY-922 on lung endothelial cells.
Western Blot analysis of (A) phosphorylated Cofilin (pCofilin) and Cofilin (B) phosphorylated MLC2 (pMLC2) and MLC2 after 24 hours treatment of BPAEC with either KIF (5 μM) or vehicle (0.1% DMSO) and post-treatment with AUY-922 (2 μM) or vehicle (0.1% DMSO) for 16 hours. The blots shown are representative of 4 independent experiments. The signal intensity of the bands was analyzed by densitometry. Protein levels of pCofilin and pMLC2 were normalized to Cofilin and MLC2 respectively. *P < 0.05, **P<0.01 vs vehicle. Means ± SEM. Western Blot analysis of (C) phosphorylated MLC2 (pMLC2) and MLC2 after 24 hours treatment of HuLEC with either KIF (5 μM) or vehicle (0.1% DMSO); and post-treatment with AUY-922 (2 μM) or vehicle (0.1% DMSO) for 16 hours. The blots shown are representative of 3 independent experiments. The signal intensity of the pMLC2 was analyzed by densitometry. Protein levels of pMLC2 were normalized to MLC2. *P<0.05 vs vehicle. Means ± SEM. (D) Confluent monolayers of BPAEC were pre-treated with either vehicle (0.1% DMSO) or KIF (25 μM) (red arrow) for 18 hours, followed by treatment with either vehicle (0.1% DMSO) or 5 μM of AUY-922 (green arrow). A gradual increase in endothelial permeability (reduced TEER) was observed in KIF treated cells (red line). AUY-922 significantly reduced the endothelial permeability (increased TEER) in both KIF-pretreated (blue line) and vehicle-treated cells (green line). (E) Cells were incubated with either VEH (0.1% DMSO) or KIF (0.01, 0.1, 1, 10, 100, 200 μM) or AUY-922 (0.01, 0.1, 1, 10, 100, 200 μM) for 24 hours. Cellular viability was evaluated by employing the MTT assay. ***P<0.001 vs VEH, n=3. Means ± SEM.