Figure 1.
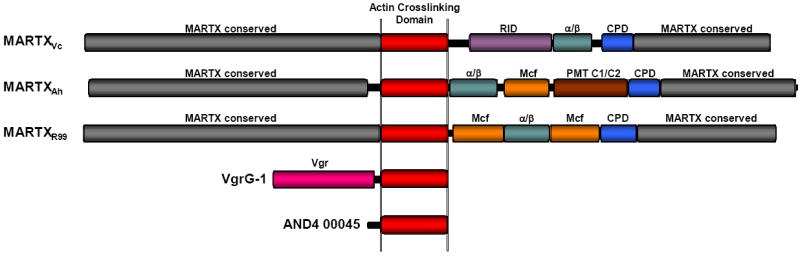
Actin crosslinking toxins. Scaled diagrams of the five known and putative actin crosslinking toxins. MARTX toxins of V. cholerae (MARTXVc), A. hydrophila (MARTXAh), and V. vulnificus Biotype 2 virluence plasmid pR99 (MARTXR99). Conserved MARTX repeat regions (grey) are predicted to converge at the eukaryotic plasma membrane to form a pore through which the centrally-located effectors are translocated. After translocation, the cysteine protease domain (CPD) initiates autoprocessing to release effectors, including the actin crosslinking domain (ACD-red), Rho-inactivation domain (RID-purple) [24], α/β hydrolase effector (α/β-green), Mcf conserved effector of unknown function (Mcf-orange), and Pastuerella multocida toxin conserved effector of unknown function (PMT C1/C2-brown)[12]. Note that MARTXR99 has a duplication of the Mcf effector. V. cholerae VgrG-1 is an effector of the V. cholerae VAS T6S system. The Vgr conserved domain (Vgr-pink) forms part of the translocation apparatus for transfer of the ACD across the phagosomal membrane after engulfment by phagocytes. Vibrio sp. AND4 hypothetical protein AND4_00045 is a putative stand-alone actin crosslinking toxin that is potentially an effector of an unknown transport apparatus.
