Figure 2: Molecular effects of representative COQ8A variants.
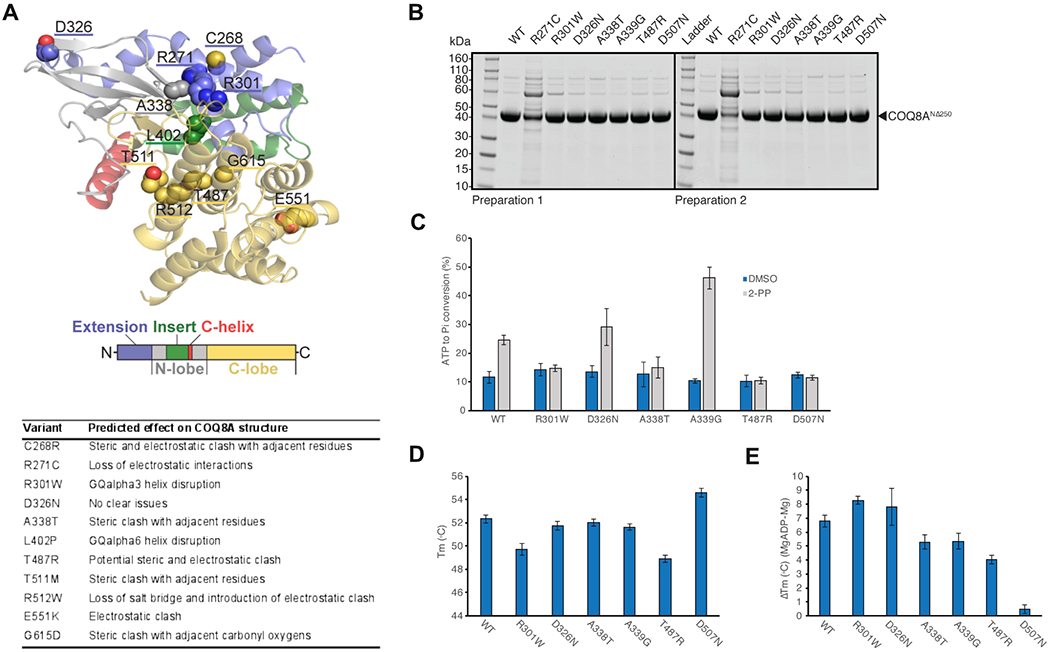
(A) 3D modelling of protein structure and function, revealing steric and electrostatic clashes or lost interactions for representative COQ8A variants. Missense variants cluster around the active size of COQ8A, except for 3 variants including E551K. (B) SDS-PAGE analysis of purified wildtype (WT) and mutant COQ8ANΔ250. Protein stability and folding was severely impaired in R271C, leading to purification failure in two preparations. (C) Compared to wildtype (WT), ATPase activity was impaired in variants affecting presumed non-catalytic (R301W) and catalytic regions (A338T, T487R) of the active site. Positive control: A339G, negative control: D507N. (D) Decrease in melting temperature (Tm) of purified COQ8A indicating moderate protein destabilization in R301W and T487R. (E) ADP nucleotide binding, which increases Tm, is impaired in A338T and T487R, but not in R301W. Note that VUS D326N is not predicted to lead to detrimental structural effects (A) and consistently yields results similar to WT in all experiments (B-E).
