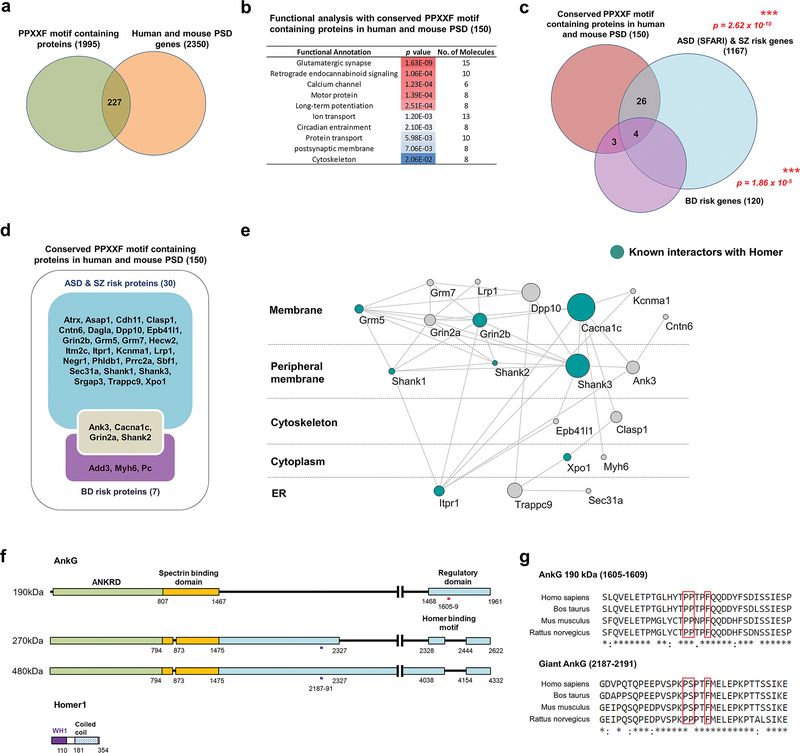
Fig. 1. Multiple postsynaptic psychiatric risk factors include a Homer1 binding motif.
a. Diagram of PPXXF motif-containing proteins in PSD. b. Functional analysis of conserved (in human, bovine, mouse, and rat) PPXXF motif-containing proteins in PSD. c. Enrichment of BD, ASD, and SZ risk factors (identified through GWAS, SFARI gene archive and de novo studies, respectively) among PPXXF motif-containing proteins in the combined human and mouse PSD. ***, p < 0.001; hypergeometry test. d. Diagram of PPXXF motif-containing proteins in the PSD is encoded by psychiatric risk genes. e. Protein interaction network generated from the list of PPXXF motif-containing PSD proteins is encoded by psychiatric risk genes in (d). The representative majority of a subnetwork is visualized and annotated by Cytoscape. The size of node indicates betweenness centrality. Known interactors with Homer1/2/3 from BioGrid and text mining were colored emerald. Edges indicate known and predicted protein-protein interactions, including experimental data from the STRING database. f. Schematic representation of the Homer1 recognition motifs in ankyrin-G (190, 270, and 480 kDa) isoforms. g. Amino acid sequence alignment of human, bovine, mouse, and rat ankyrin-G regions containing the Homer-binding motif PPXXF. Sequence alignments were performed by Clustal Omega. SFARI : Simons Foundation Autism Research Initiative.