Figure 1. Experimental design and mouse developmental screen.
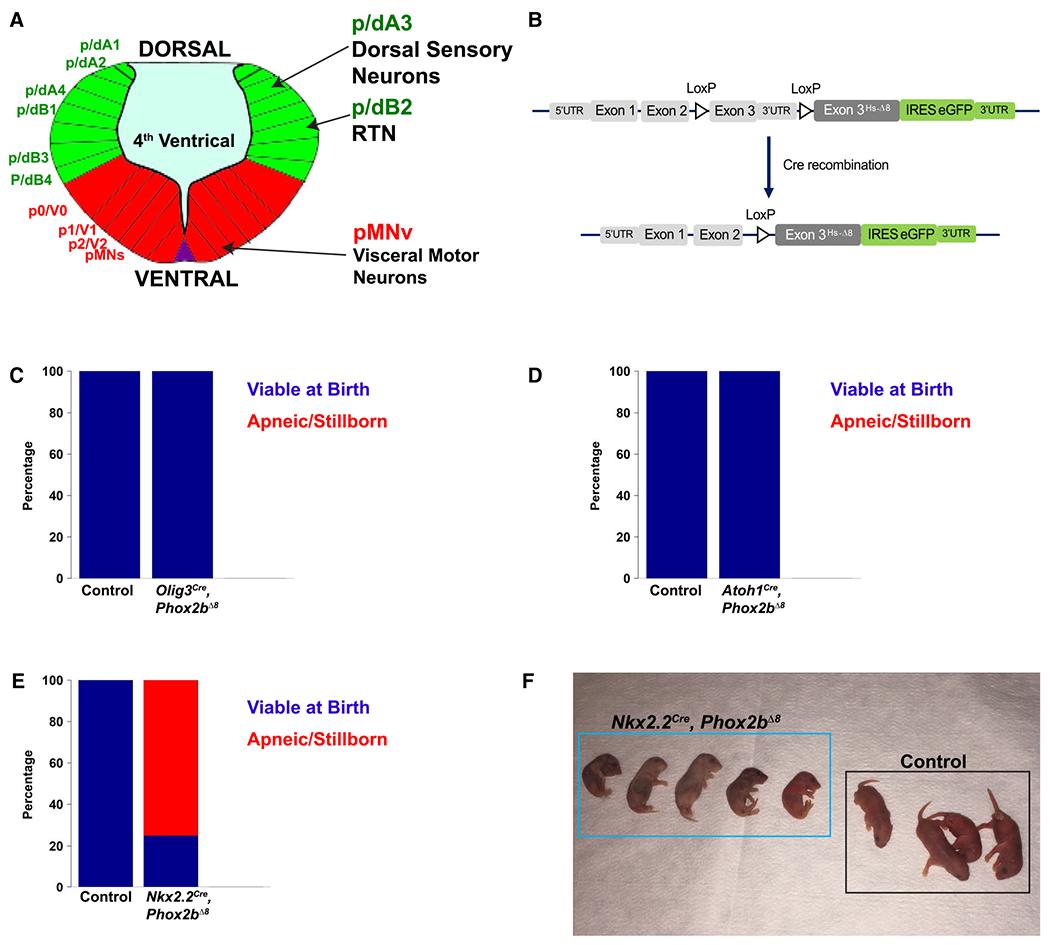
A. Artistic rendering of rhombomere 4 of an E10.5 mouse embryo. The developing rhombencephalon can be subdivided into dorsal progenitor domains (green) and ventral domains (red). Within each domain, specific neuronal and glial populations are generated. Phox2b is expressed in 3 progenitor domains depicted on the right: dA3, dB2, and pMNv. These progenitor domains give rise to dorsal sensory neurons, retrotrapezoid nucleus RTN, and visceral motor neurons, respectively. B. Transgenic mouse strategy. The humanized NPARM Phox2b mouse mutation is located in exon 3. Cre-mediated recombination replace the endogenous murine exon 3 with a human exon3 harboring an eight-nucleotide deletion (Hs-Δ8). C-E. Developmental screen of mice to identify apneic/stillborn presentations. Stacked bar graphs show proportion of pups viable at birth in blue, with apneic/stillborn pups in red. Genotype is denoted on the bottom of each bar graph. This screen (C) derives from 28 control pups and 44 mutant pups spread over 10 litters, (D) derives from 10 control pups and 18 mutant pups spread over six litters, (E) derives from 10 control pups and 12 mutant pups. (F) Photograph of a representative Nkx2.2Cre, Phox2bΔ8 litter showing absent or limited respiratory movements and cyanosis at birth.
