Figure 5. Lineage tracing of Nkx2.2/Phox2b-derived and Phox2b-derived cells.
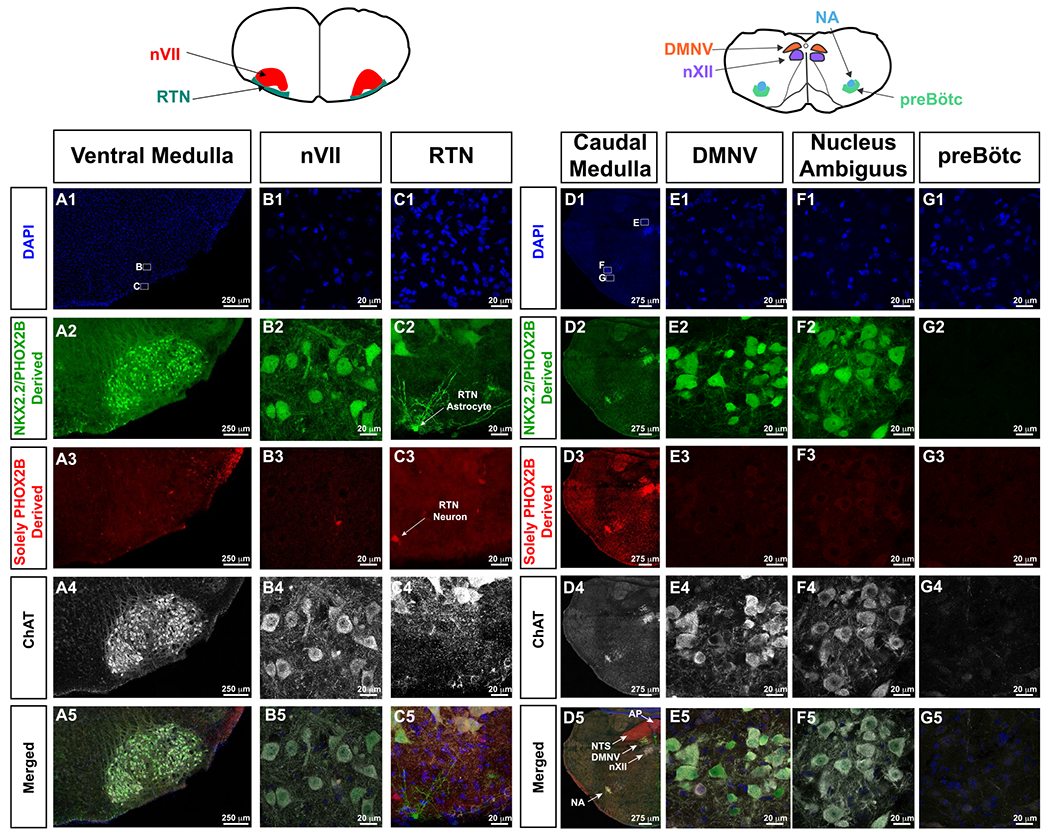
For orientation, cartoons of brainstem anatomy are illustrated atop of the panels, with left cartoon pertaining to A-C, whereas right cartoon pertains to d-g. In this intersectional approach, GFP expressing cells show derivation from both Nkx2.2 and Phox2b expressing cells (second row from top), and tdTomato expressing cells are solely derived from PHOX2B expressing progenitor cells (third row from top). ChAT (white in fourth and fifth row from top) highlights cholinergic neurons. In A1 and D1, small white boxes delineate where the high magnification photomicrographs in the respective panels were obtained. In Panel C2, white arrow indicates a Nkx2.2-derived, Phox2b-derived astrocyte. Panel C3, white arrow indicates Phox2b-derived RTN neuron. Panel D5 shows the anatomy of key medullary structures including area postrema (AP, Phox2b-derived, ChAT-negative), nucleus of the solitary tract (NTS, Phox2b-derived, ChAT-negative), dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus (DMNV, Nkx2.2/Phox2b-derived, ChAT-positive), hypoglossal nucleus (nXII, not derived from Phox2b nor Nkx2.2, ChAT-positive), and nucleus ambiguus (NA, Nkx2.2/Phox2b-derived, ChAT-positive). RTN neurons are not derived from Nkx2.2, and preBötC neurons, which do not express tdTomato nor GFP do not show Nkx2.2 nor Phox2b derivation.
