Figure 4. Allele frequency distribution of GWAS selected variants and LD tagging of causal variants.
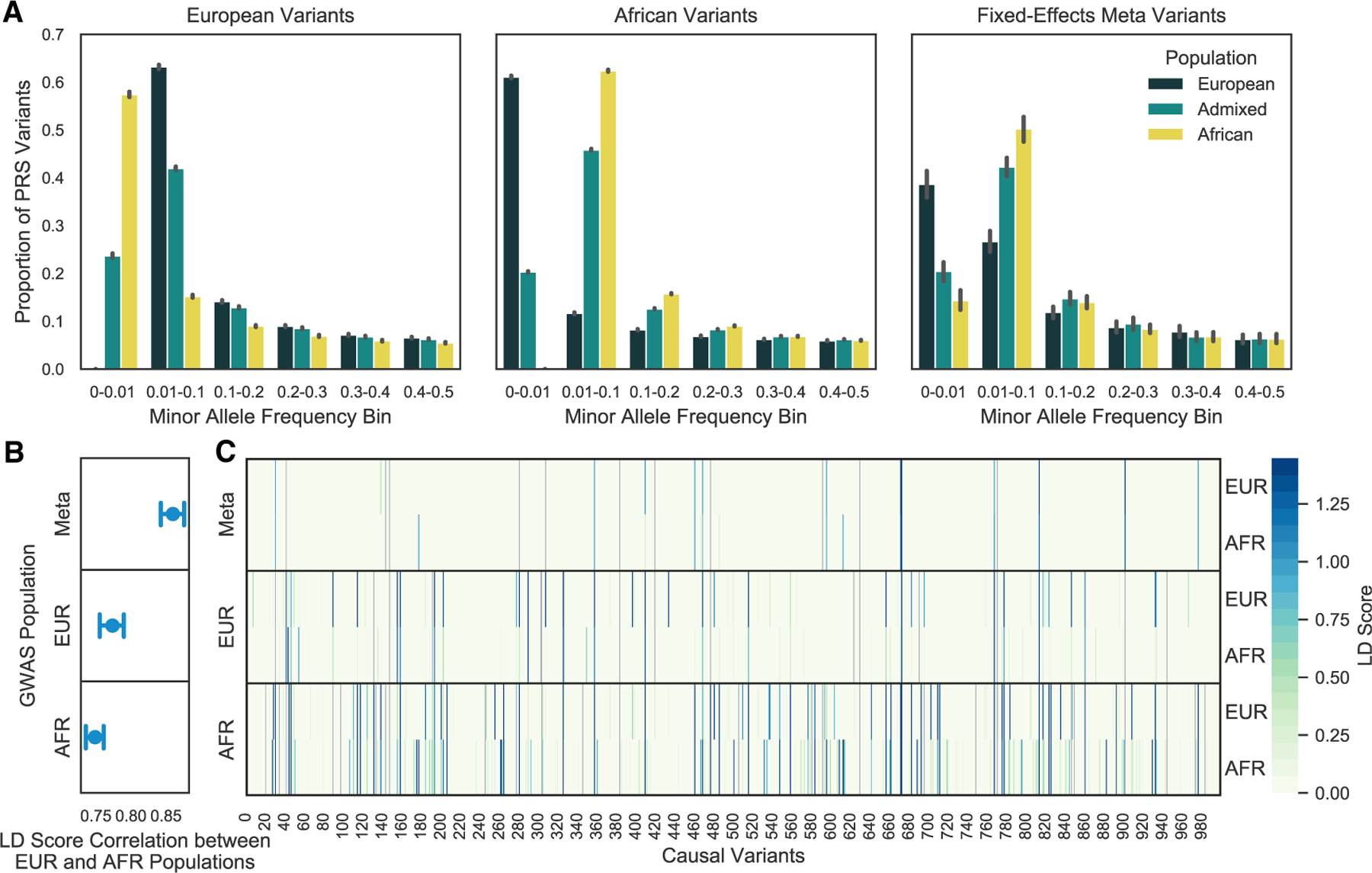
GWAS significant variants are more common in the study population from which they were discovered; however, African Ancestry GWAS variants may result in better LD tagging across populations. Variants were selected from a European or African ancestry GWAS or a fixed-effects meta-analysis of both populations.
(A) GWAS variants were binned by their MAF estimated from the European, African, and admixed populations. The error bar represents the 95% CI across simulations.
(B) LD scores were calculated for every causal variant by adding up the LD r2 for each GWAS tag variant within ±1,000 kb of the causal variant. LD scores calculated in a Europeans and Africans were compared by Pearson’s correlation. The results were summarized across simulations as the average and 95% CI.
(C) Raw LD scores for each causal variant (m 1,000) calculated in a European or African population for one simulation. Each panel shows the approach used for variant selection. Causal variants directly discovered through the GWAS are colored in gray.
