Fig. 7.
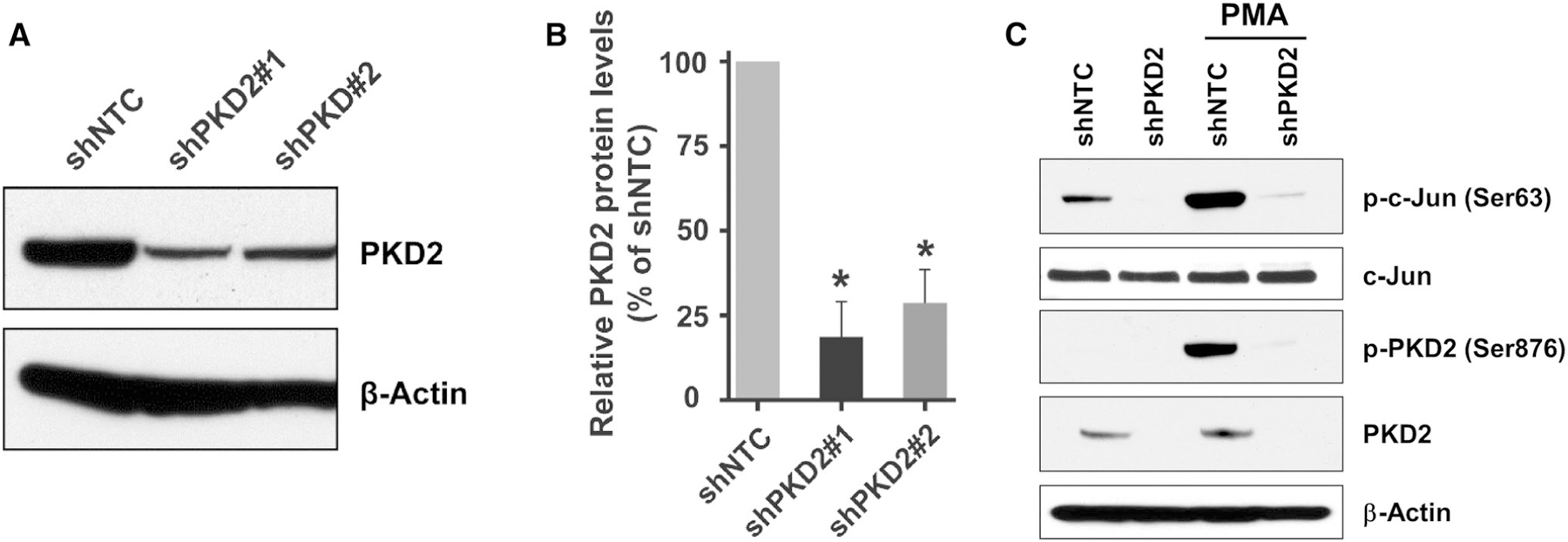
Knockdown of PKD2 gene expression in urothelial bladder carcinoma cells. a UMUC1 cells stably transduced with lentivirus coding for human shRNA sequences for PKD2 and non-target control were used for analysis of PKD2 expression. Total cellular protein was extracted from these cells, and a total of 80 μg cell extract protein was analyzed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting with an antibody against PKD2 or β-actin to verify equal loading. b Quantitation of the PKD2 protein levels in shPKD2#1 and shPKD2#2 transduced cells comparing cells transduced with shNTC, n = 3. Error bars denote variation in biological replicates. c Validation of PKD2 knockdown efficiency in shPKD2 transduced cells. UMUC1 cells transduced with shPKD2#1 or shNTC were incubated with or without 200 nM PMA for 30 min and lysed. Total protein was extracted, and PKD2 and c-Jun protein level and activity were analyzed by western blotting with the anti-PKD2, phospho-PKD2 (Ser876), c-Jun, phospho-c-Jun (Ser63), or β-actin antibodies, respectively. shNTC, non-target control; shPKD2#1, PKD2 clone 1; shPKD2#2, PKD2 clone 2; PMA, Phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate
